The illegal wildlife trade (IWT) is a large-scale transnational organized crime that drives corrupt activities, threatens biodiversity, and can significantly impact public health. Criminal syndicates involved in wildlife-related offenses are well-organized and adapt their methods in line with technological advancements. IWT ranks as the 7th largest criminal enterprise, following narcotics, counterfeiting, and human trafficking.
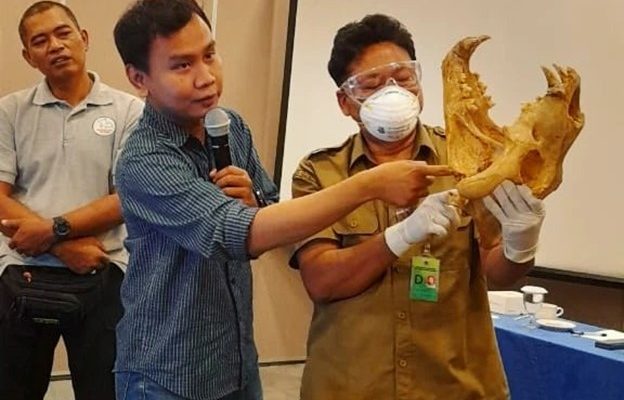
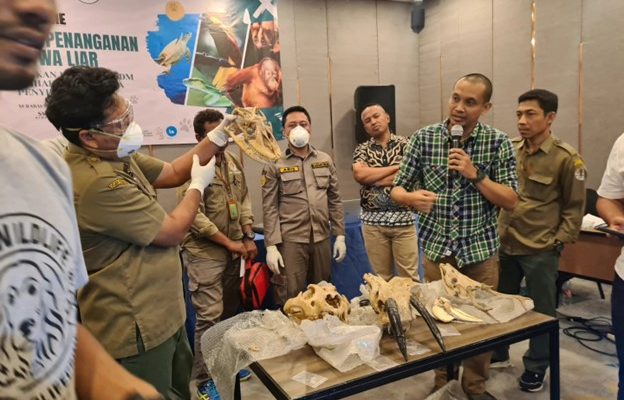
Apart from live wild animals, many deceased specimens and their parts are also confiscated. Proper handling of deceased wildlife and their parts is essential to prevent damage during storage, and following proper procedures is necessary for sampling to conduct DNA tests as evidence to determine whether the parts belong to protected species. This signifies that efforts to oversee the illegal wildlife trade still require further reinforcement through collaborations with relevant parties. Based on this premise, the Indonesian Wildlife Network organized an integrated training activity at ports and airports on August 14-16 in Surabaya and August 21-22 in Jakarta. The training was attended by multiple stakeholders including the Nature Conservation Agency (BKSDA), Animal Quarantine Center, Police, Prosecutor’s Office, and Aviation Security.
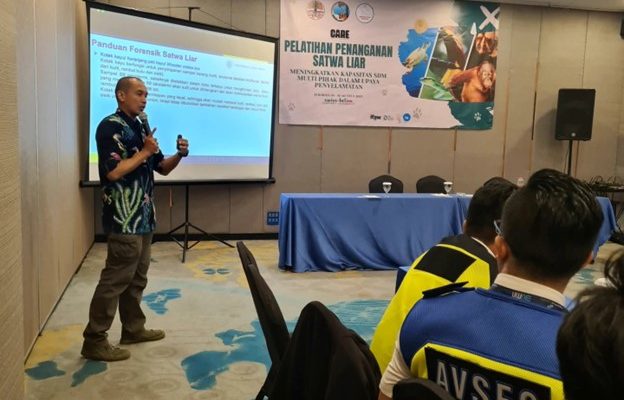
Two lecturers from the Animal Systematics Lab were invited as speakers for this training: Donan Satria Yudha, S.Si., M.Sc., and Dr. Dwi Sendi Priyono, S.Si., M.Sc. Both of them possess extensive experience in the field of wildlife forensics and have made significant contributions to the development of scientific knowledge related to wildlife conservation and protection in Indonesia. Donan Satria Yudha, B.Sc., M.Sc., explained the principles of sample collection for morphological analysis, providing examples of various cases that have been worked on for forensic investigations. Dr. Dwi Sendi Priyono, B.Sc., M.Sc., explained the principles and techniques of collection, as well as DNA analysis, to uncover various cases of wildlife trade.
This wildlife forensics training is expected to enhance multi-sectoral coordination and cooperation in both implementing regulations and enforcing the law. It aims to align perceptions regarding the handling of wildlife evidence and its parts, one of which involves applying the CARE standards. This approach allows greater chances for surviving wildlife post-confiscation by providing basic training in handling, care, and insights into wildlife and their needs.