On July 16 and 17, 2024, a research team from the Faculty of Biology at Gadjah Mada University (UGM), led by Prof. Dr. Ratna Susandarini, M.Sc., conducted an ethnobotanical survey as part of a collaborative effort on the Bioprospecting of Medicinal Plants with the Mount Merbabu National Park Authority. The survey took place in the Ampel and Kopeng Resorts within the Mount Merbabu National Park.
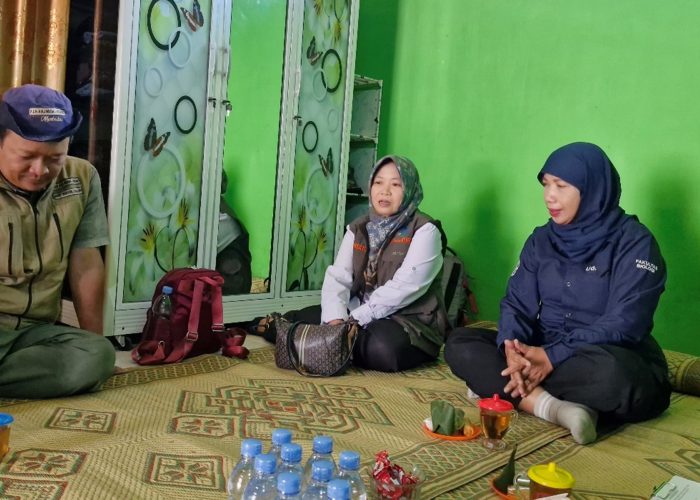
The primary objective of this collaboration is to gather data on the use of medicinal plants by the local communities living around the national park. This initiative is crucial for the conservation of biodiversity and the sustainable use of natural resources. The research team collected information through interviews with local residents, who shared their traditional knowledge on the medicinal properties of various plants.
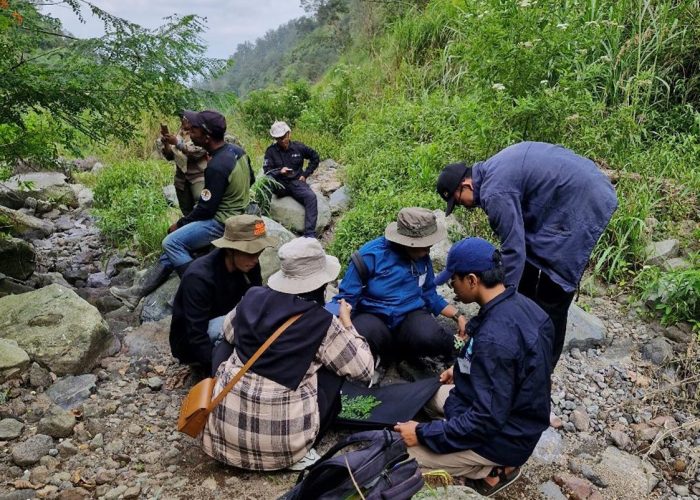
Following the data collection from the community, the team conducted a field survey to collect samples of the medicinal plants mentioned. This fieldwork is essential for the bioprospecting process, which aims to identify plants with potential biomedical applications. The collected samples will be analyzed in the laboratory to determine their chemical composition and potential health benefits.
Prof. Dr. Ratna Susandarini emphasized the importance of this research in contributing to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly in the areas of health, biodiversity conservation, and sustainable use of ecosystems. “Our work here not only aims to discover new medicinal compounds but also to promote the conservation of plant biodiversity in Mount Merbabu National Park,” she stated.
The collaboration between UGM and the Mount Merbabu National Park Authority is a significant step towards integrating traditional knowledge with modern scientific research. This approach not only respects and preserves the cultural heritage of the local communities but also enhances the scientific understanding of medicinal plants.
The Mount Merbabu National Park, known for its rich biodiversity, provides an ideal setting for this type of research. The park is home to numerous plant species, many of which have been used traditionally for medicinal purposes. By documenting and studying these plants, the research team hopes to contribute to the global knowledge of medicinal biodiversity.
The local communities play a vital role in this research. Their traditional knowledge and practices are invaluable resources for identifying plants with medicinal properties. The involvement of the community also ensures that the benefits of the research are shared with those who have preserved this knowledge for generations.
The field survey in the Ampel and Kopeng Resorts was conducted with the support of the Mount Merbabu National Park Authority, which provided logistical assistance and access to the research sites. This collaboration highlights the importance of partnerships in achieving conservation and sustainable development goals.
The findings from this research will be published in scientific journals and shared with the local communities and relevant stakeholders. This dissemination of knowledge is crucial for promoting the conservation of medicinal plants and their sustainable use.
In conclusion, the bioprospecting survey of medicinal plants in Mount Merbabu National Park is a significant initiative that combines traditional knowledge with modern science. It aims to contribute to the conservation of biodiversity, the discovery of new biomedical compounds, and the sustainable use of natural resources, aligning with the broader goals of the SDGs.