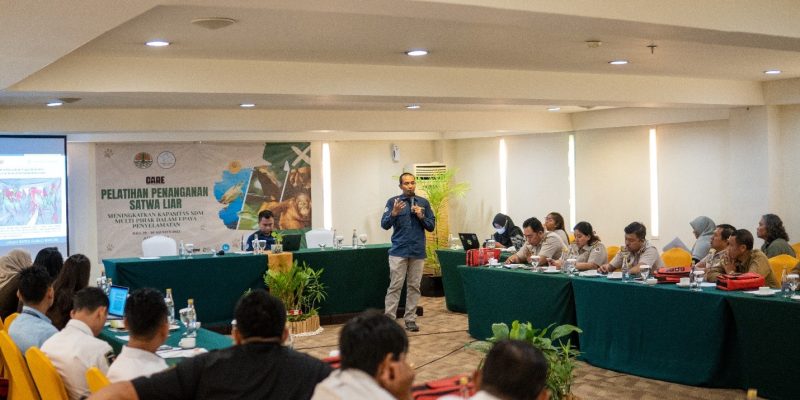
Following the successful execution of the “Wildlife Handling Training” series by the Indonesian Wildlife Network (JSI) in Surabaya and Jakarta, the initiative continued to the regions of Bali and Lampung. This endeavor holds great significance due to the severe threat posed by illegal wildlife trade to biodiversity, as well as its potential to fuel corruption among involved government officials. Wildlife trade typically occurs through a country’s points of entry and exit, thus, the “gatekeepers” are equipped to heighten vigilance, aiming to curtail and even thwart illegal wildlife trade, particularly that protected by Indonesian law.
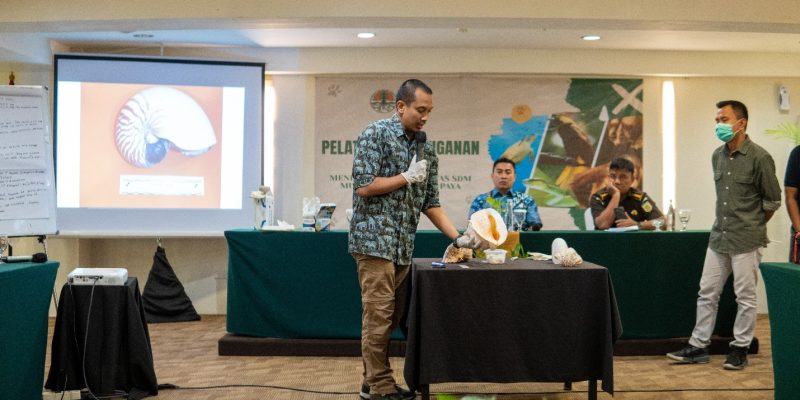
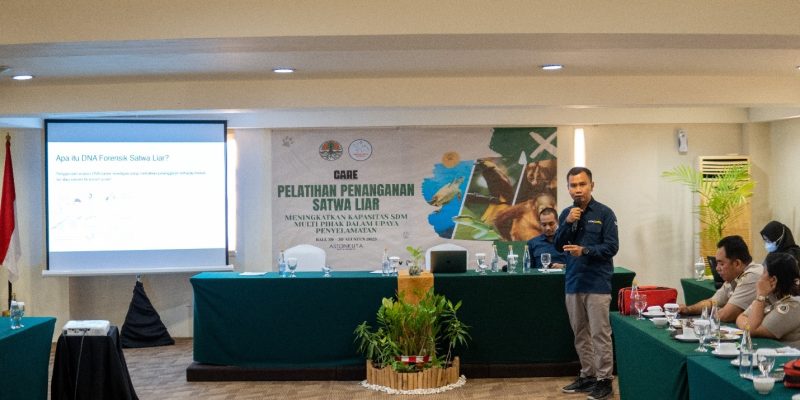
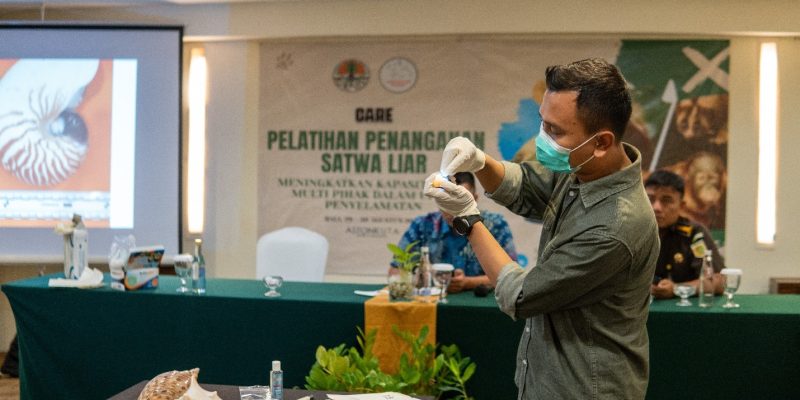
The Indonesian Wildlife Network conducted integrated training sessions in Bali on August 29-30, 2023, at the Aston Kuta Hotel, and on September 7-8, 2023, at the Swissbell-Hotel Lampung. The sessions were attended by a diverse group including BKSDA, the Prosecutor’s Office, the Police, Avian Security, the Animal Quarantine Center, and regulatory agents. The training covered various aspects of forensic examination on deceased wildlife and their parts. Proper handling is crucial to prevent damage during storage. Additionally, understanding the procedures for species identification is imperative. This encompasses morphological, anatomical, and molecular (DNA testing) identification methods. Collecting DNA samples serves as evidence to determine if the wildlife parts in question are protected by law or not. Serving as speakers were Faculty of Biology UGM lecturers and alumni: Donan Satria Yudha, S.Si., M.Sc, and Dr. Dwi Sendi Priyono, S.Si., M.Si. from the Animal Systematics Laboratory. Donan and Sendi possess extensive experience in wildlife forensic science and have made significant contributions to the advancement of knowledge in wildlife conservation and protection in Indonesia. Donan Satria Yudha, S.Si., M.Sc explained the principles of sample collection for morphological analysis, providing examples of various cases worked on for forensic investigation. Dr. Dwi Sendi Priyono, S.Si., M.Si., elucidated the principles and techniques of collection to DNA analysis, unveiling various cases of wildlife trade. One notable alumni of the Faculty of Biology UGM is AKBP Sugeng Irianto class of 1987, currently serving as the Head of Sub-Division 5 in the Directorate of Industry and Commerce Crime Investigation (Dittipidter) at the Indonesian National Police Criminal Investigation Department (Bareskrim Polri). i. He elaborated on the “Dynamics of Protected Wildlife Case Handling.”
The Wildlife Forensic Training serves as a platform for sharing knowledge, experiences, and discussions on the latest developments regarding regulations and lessons learned from supervisory efforts. It is also expected to enhance multi-stakeholder coordination and cooperation, both in implementing regulations and enforcing the law. Additionally, it aims to standardize perceptions regarding the handling of wildlife evidence and their parts, one approach being the application of CARE standards, which enables a greater chance for the survival of wildlife post-seizure, through basic handling training, care, and understanding of wildlife and their needs. This integrated training is anticipated to bring about a renewal in efforts to monitor the utilization and circulation of wildlife in the future.
The Wildlife Forensic Training contributes to several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 15: Life on Land and SDG 16: Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions. SDG 15: Life on Land signifies that this training aids in safeguarding biodiversity and terrestrial ecosystems by investigating cases of illegal hunting, wildlife trade, and other violations against wildlife. It contributes to the goal of maintaining sustainable terrestrial ecosystems. SDG 16: Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions entails that this training plays a role in combating illegal wildlife trade and strengthening relevant laws and regulations. It supports the objective of creating robust institutional coordination to address this issue. The Wildlife Forensic Training is vital in protecting endangered wildlife and maintaining ecosystem balance, ultimately contributing to the overall goals of sustainable development.