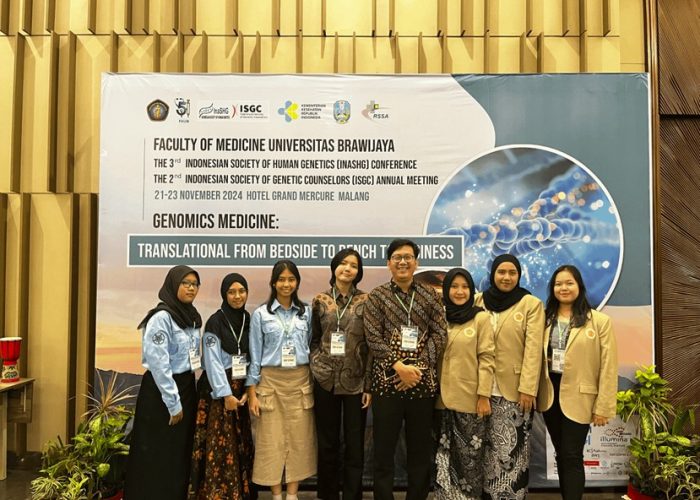
Undergraduate students from the Faculty of Biology at Gadjah Mada University—Alifia Nur Hidayah, Ardiza Puspa Rahmaningtyas, Farah Ayu Kamayani, Hana Magista Qathrunnada, Tazkia Mahsya Syavira, and Luisa Ramyahastri Paramatatya—participated in an international human genetics conference. This conference was the 3rd Indonesian Society of Human Genetics (InaSHG) Conference, held simultaneously with the 2nd Indonesian Society of Genetic Counselors (ISGC) Annual Meeting 2024. In collaboration with the Faculty of Medicine at Brawijaya University, the event took place from November 21-23, 2024, at the Grand Mercure Hotel, Malang. With the theme “Genomics Medicine: Translational from Bedside to Bench to Business,” the conference emphasized a comprehensive approach to the development of medical genetics. The program included research presentation sessions aimed at disseminating the latest research advancements, innovations in clinical practice, and developments in genetics policy. These sessions were designed to optimize knowledge exchange, strengthen interdisciplinary collaboration, and enhance the professional competence of participants. The conference also featured symposia with speakers from prominent national and international genetics experts.
During the event, students under the supervision of Prof. Dr. Niken Satuti Nur Handayani, M.Sc., and Indra Lesmana, S.Si., M.Sc., presented their research on the development of a Long-read Sequencing Application for Genotyping Hereditary Diseases in Humans. This research aims to develop an efficient genetic screening methodology for detecting various hereditary diseases, focusing on hemophilia A, obesity, thalassemia, and atopic dermatitis using long-read sequencing technology developed by Oxford Nanopore Technologies. The students gained valuable experience presenting their research at an international scientific forum, honed their scientific communication skills, and were inspired to further develop their research and broaden their knowledge about the latest advancements in genomics.
This research has significant implications, not only in academic contexts but also in supporting the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly Goal 3, which focuses on Good Health and Well-being. The contribution of this research to the development of genetics-based healthcare services represents a strategic step toward advancing the health system. The implementation of the developed technology is expected to have substantial impacts in several areas: optimizing preventive efforts and the management of genetic diseases, improving life expectancy for populations, and ensuring equitable, sustainable access to modern healthcare technologies.