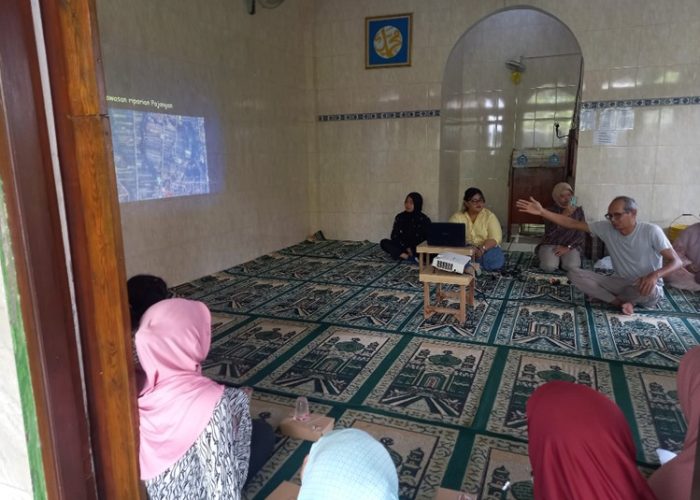
On October 5, 2024, Mr. Susilohadi, S.Si., M.Si., Ph.D., from the Faculty of Biology, Universitas Gadjah Mada, conducted a socialization on the definition, role, and management of riparian zone, particularly concerning conservation, to the residents of Pajangan Hamlet, Wedomartani, Ngemplak, Sleman, Yogyakarta. This event was part of a series of activities under the 2024 Program Hibah Desa Mitra in Wedomartani Village, Ngemplak, Sleman, Yogyakarta.
The event began with an explanation regarding the definition of a riparian zone. Riparian zones are narrow and elongated areas that act as a transition between aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. For people living in rural areas, the riparian zone is the only “forest” remaining amidst settlements and rice fields, which occupy nearly 90% of the village area. The role of the riparian zone is crucial, not only as a buffer zone between water and land but also as a carbon sink, erosion preventer, water filter, soil health maintainer, a place for natural vegetation to grow, and a habitat for various wildlife species.
On this occasion, Mr. Susilohadi, S.Si., M.Si., Ph.D., as the speaker, emphasized that the role of riparian zone for the community has become even more important, given that many of these areas are being converted, particularly due to the expansion of housing developers and the emergency state of waste management. In Yogyakarta city and Sleman Regency, environmental crimes such as the uncontrolled disposal of domestic and industrial waste around riparian zones are widespread. This socialization also aligns with SDG (Sustainable Development Goal) number 15, which focuses on the management of terrestrial ecosystems, including specific goals like the protection of protected areas, water flow management, vegetation restoration, wildlife rehabilitation, waste and pollution management, as well as community education and participation. Community participation, especially from Pajangan Hamlet in Wedomartani, in this socialization event was quite large and enthusiastic, particularly with the active involvement of women who participated in discussions about the future of the river and its borders in their village, considering it as part of the local community’s ecosystem.