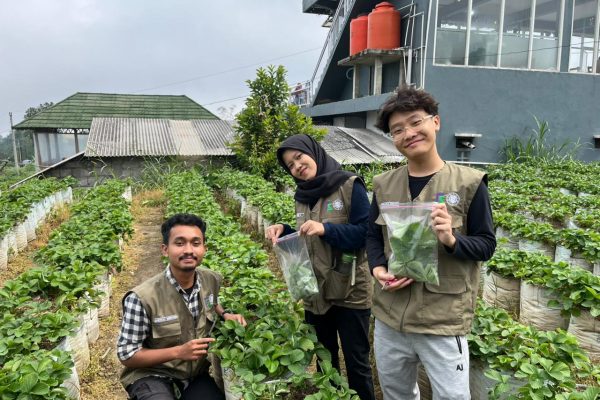
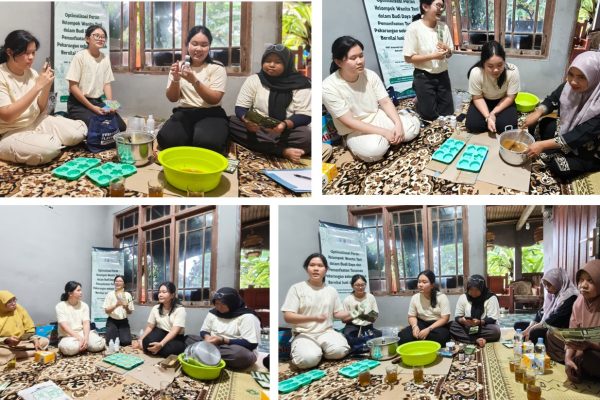
A research team from the Faculty of Biology at Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), led by Ganies Riza Aristya, Ph.D., has achieved a significant milestone in Indonesian strawberry genomic research by successfully uncovering and characterizing the complete chloroplast genome of the superior local strawberry cultivar, ‘Mencir’. This research, funded by a Fundamental Basic Research Grant from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Research, and Technology, successfully optimized a high-quality DNA extraction method using a modified CTAB buffer, yielding DNA with optimal purity and concentration for next-generation sequencing. Nanopore sequencing technology using the ONT PromethION platform successfully generated comprehensive chloroplast genomic data, with a total length of 155,568 base pairs, which was then assembled and annotated comprehensively.
In-depth analysis of the genome revealed the structure and organization of critical genes involved in photosynthesis and chloroplast gene regulation, namely the ndh, pet, and rpo gene groups. The mapping of exon-intron structures, analysis of conserved motifs, and 3D protein structure predictions successfully provided detailed insights into the complexity and uniqueness of each gene group. Furthermore, the research team, which includes three Faculty of Biology students—Tika Nur Amini, Andreas Wibisono, and Tan Rendy—also conducted a robust phylogenetic analysis, confirming strong kinship relationships among species within the Rosaceae family and strengthening the understanding of the evolutionary history and chloroplast inheritance patterns in the commercial hybrid strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa).
This research activity has not only produced highly valuable foundational data but has also yielded several tangible outputs, including two research publications in reputable international journals, as well as dissemination videos and posters. Synergistic collaboration with local partners—such as Inggit Strawberry Agritourism in Magelang and Sleman—and the genomics industry partner Integrated Genome Factory (IGF), has enriched the research process and ensured the applied relevance of the achieved results.
Strategically, this research achievement provides a solid scientific foundation for strawberry breeding programs based on molecular markers and gene editing technologies such as CRISPR/Cas9. In the second year, the research will focus on the functional validation of candidate genes and the identification of quantitative trait loci (QTL) for important agronomic traits, such as disease resistance and photosynthetic efficiency, which can be directly utilized by plant breeders.
Finally, this research activity directly contributes to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 2: Zero Hunger, Achieving Food Security and Improved Nutrition, and Promoting Sustainable Agriculture. By developing superior strawberry varieties that are more productive, stress-tolerant, and adaptive to local conditions, this research promotes a more resilient and sustainable agricultural system. Additionally, through enhancing the capacity of local human resources and transferring knowledge to farmers (SDG 4: Quality Education), as well as inclusive multi-stakeholder collaboration (SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals), this research serves as a tangible example of how genomic science can be directed to support food sovereignty, community empowerment, and sustainable and equitable agricultural development in Indonesia.