Arsip:
Innovation
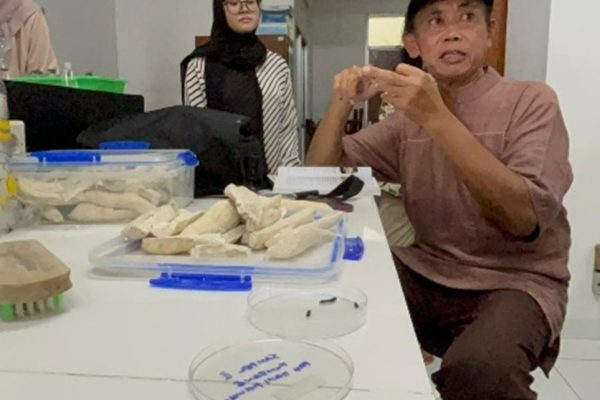
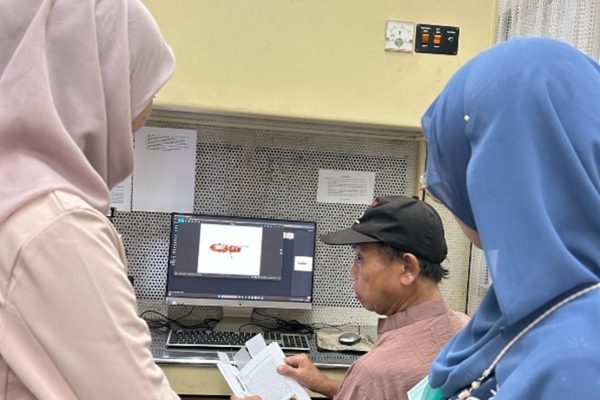
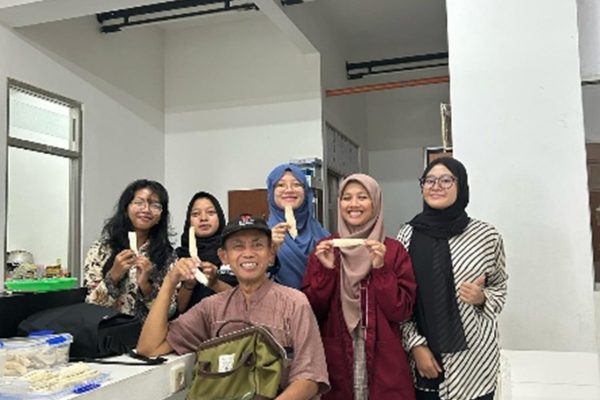
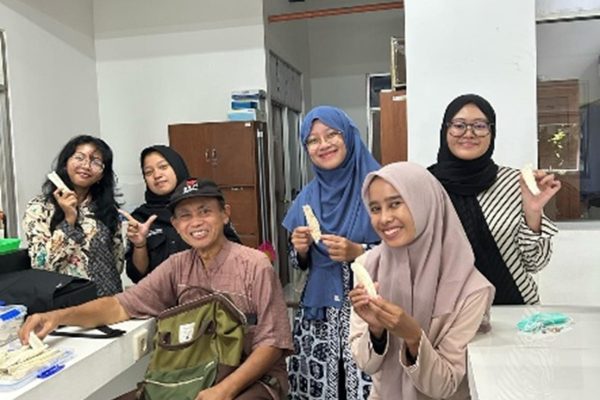
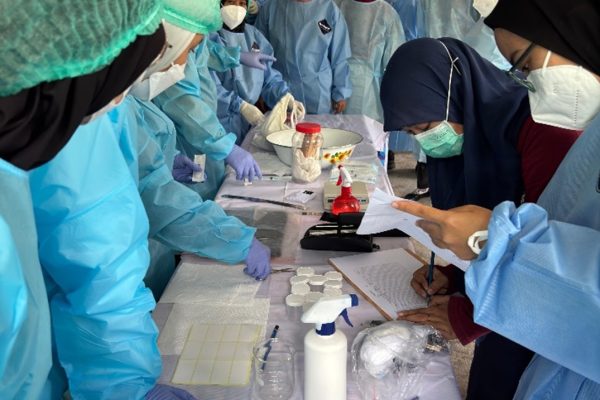
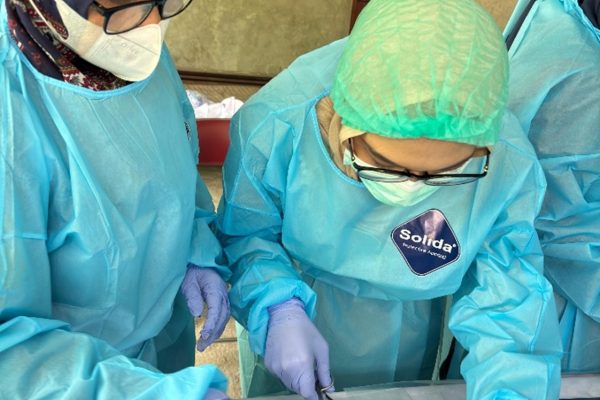
The Faculty of Biology, Universitas Gadjah Mada, through the Animal Developmental Structure Laboratory (SPH), successfully held its first batch of animal microtechnique training on April 22–24, 2025. The training was attended by five participants, comprising three doctoral students and two undergraduate students from the Faculty of Biology, UGM.
Head of the SPH Laboratory, Dr. Ardaning Nuriliani, S.Si., M.Kes., emphasized the importance of this training as a platform to strengthen laboratory skills and foster cross-level academic knowledge sharing.
“This training represents a concrete contribution from the Faculty of Biology, UGM, in equipping students with applicable and relevant microtechnique skills for biological research. Insyaa Allah, we plan to organize this training in 2 to 3 batches each year,” said Dr. Ardaning.
The training included both theoretical sessions and hands-on practicals, focusing on the preparation of histological slides using the paraffin method—one of the fundamental techniques in microtechnique. Participants were guided by a teaching team consisting of seven lecturers and two laboratory technicians from the SPH Laboratory. All participants demonstrated strong enthusiasm, actively engaged in discussions, and showed great interest in each session.
Beyond serving as a competency-enhancing activity, this training also contributes to achieving Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) No. 4 on quality education. Through this initiative, the Faculty of Biology UGM hopes to continuously support the advancement of education quality, particularly in mastering specific technical skills in the field of biology.
Moreover, this microtechnique training is expected to become an inspiring example for other educational institutions in developing practice- and research-based learning, in pursuit of producing excellent and globally competitive graduates.
Prof. Dr. Niken Satuti Nur Handayani, M.Sc., a genomics researcher from the Faculty of Biology at Universitas Gadjah Mada, together with the Satria Budi Dharma Setia Foundation (YSDS), and genomics researchers from IPB University, Universitas Mataram, and Universitas Swadaya Gunung Jati (UGJ), participated in an event organized by Pacific Biosciences held on April 14–16, 2025, at the Hyatt Regency Danang Resort and Spa, Da Nang, Vietnam. Participation in PrIMS 2025 is not only about sharing research findings, but also about learning from the global scientific community and establishing international partnerships to accelerate the adoption of genomic sequencing technologies in Indonesia in response to increasingly complex research challenges.
PacBio PrIMS 2025 brought together experts, scientists, and professionals in the field of genome sequencing from various countries across the Asia-Pacific region, covering key topics such as Plant, Animal & Microbial Genomics, Human Genomics, Iso-Seq & Single Cell Iso-Seq, Bioinformatics, and Emerging Applications & Technologies. Participation in PrIMS 2025 is part of a continuous effort to foster global collaboration and strengthen national genomics research capacity, which is vital for accelerating the use of next-generation sequencing technologies to address major challenges in public health and environmental sciences. This forum also provides a platform for dialogue and collaboration between Indonesian researchers and international partners in developing laboratory infrastructure, technology transfer, and cross-border scientific training. With a spirit of collaboration, Indonesia’s participation is expected to serve as a bridge toward strengthening an inclusive and globally competitive genomics research ecosystem.
Suriname, April 2025 — The delegation of the Faculty of Biology, Universitas Gadjah Mada continued the series of international engagement visits in Suriname by visiting Anton de Kom University (Anton de Kom Universiteit van Suriname). The delegation consisted of Prof. Dr. Budi Setiadi Daryono, M.Agr.Sc. as Dean, Dr. Slamet Widiyanto as Vice Dean for Finance, Assets, and Human Resources Affairs, and Dr. Eko Agus Suyono, M.App.Sc. as Vice Dean for Research, Community Service, Collaboration, and Alumni Affairs.
This visit was received directly by Kartika Doerdjan, M.Sc., Dean of the Faculty of Math and Natural Sciences, together with Dr. Irwin Hidalgo (Dean Secretary), and Dr. Irwan Molgo (Head of Biology Program). In the meeting, both parties discussed the initiation of strategic cooperation covering various fields, such as: summer course program, international conference International Conference on Biological Sciences (ICBS), further study for lecturers, visiting professors, joint lectures and research, collaborative publications, training for lecturers and students, development of shared laboratories and facilities, sandwich program, and development of greenhouse and herbarium.
In addition, the delegation also visited the International Academy Suriname (IAS) and was received by the director of IAS, Mrs. Haidy Lie A Ling. The discussion with IAS focused on further study opportunities for students at the Faculty of Biology UGM as well as scholarship opportunities that can be given to prospective international students.
The series of activities in Suriname ended with a dinner with the Embassy of the Republic of Indonesia (KBRI) in Paramaribo. On this occasion, the delegation of the Faculty of Biology UGM said goodbye to the representatives of the KBRI and expressed their appreciation for the warm welcome and support during the activities in Suriname.
This activity also became a real manifestation of the commitment of the Faculty of Biology UGM in supporting the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals, especially SDG 4 (Quality Education) by increasing access and quality of higher education across countries, and SDG 17 (Partnerships to Achieve the Goals) by strengthening global cooperation in the fields of education, research, and innovation.
Yogyakarta, March 20, 2025 – The Entomology Laboratory of the Faculty of Biology, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), conducted a training session on the Identification and Rearing of Wood and Bamboo Pest Insects. The training was attended by students, Entomology Laboratory lecturers (Drs. Hari Purwanto, M.P., Ph.D., Dr. Eng. Atikah Fitria Muharromah, S.Si., M.Eng., Aryo Seto Pandu W., S.Si., M.Sc.), and laboratory staff (Rio Tri Rahmawati, S.Si.) as part of the implementation of the KDM and Lit-MBKM Research Grant 2025.
This event featured Drs. Agus Ismanto, a researcher in wood and bamboo pests from the National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), as the main speaker. The session was officially opened by the Head of the Entomology Laboratory and continued with a presentation by Drs. Agus Ismanto. He delivered an in-depth training on rearing techniques and the identification of pest insects that commonly attack wood and bamboo, two crucial commodities in Indonesia’s handicraft industry.
According to Drs. Agus Ismanto, identifying pest insects is a crucial first step in effective pest management. During the training, participants learned various identification techniques using microscopes and other tools such as loops. They were also trained to recognize the physical characteristics of different pest species commonly found in wood and bamboo, including Dynoderus sp., Lyctus sp., and Mynthea sp.. Additionally, the session covered various solutions to combat pest infestations that could degrade the quality of wood and bamboo. These solutions included environmentally friendly methods such as soaking and boiling the wood or bamboo in water.
This training also aimed to strengthen collaboration between academics, researchers, and students in an effort to enhance understanding of the importance of protecting wood and bamboo from pest infestations, which could impact both economic and ecological sectors.
The event is expected to bring significant benefits to all participants while expanding knowledge about the role of insects as pests and the importance of entomological research in improving the quality of wood and bamboo craft commodities in Indonesia.
This training not only provided academic benefits but also contributed to achieving several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including: SDG 4: Quality Education, SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure, SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production, and SDG 15: Life on Land.
Yogyakarta, 20 February 2025 , PT Bumitama Gunajaya Agro (BGA) continues to demonstrate its commitment to advancing innovation within Indonesia’s palm oil sector through the implementation of its 2025 Open Innovation Program. The program was formally introduced during a socialization event held at the Tropical Biology Auditorium, Faculty of Biology, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), and was attended by faculty members and students.
This activity also marked the continuation of collaboration between PT BGA and the Faculty of Biology UGM in the previous year. In his opening address, Dean of the Faculty of Biology, Prof. Dr. Budi Setiadi Daryono, M.Agr.Sc., underscored the strategic importance of partnerships between academia and industry in enhancing the relevance and quality of research and innovation. He expressed appreciation for the opportunity to strengthen this partnership, noting that he was a recipient of the BGA Innovation Grant in the previous cycle.
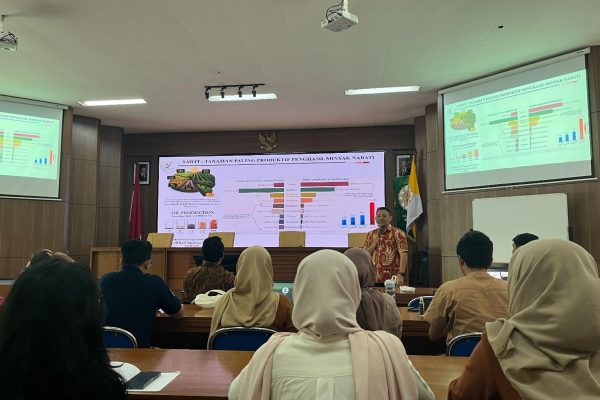
Dr. Ade Agung Laksono, Head of the Bumitama Academy Department at PT BGA, delivered the keynote presentation titled “Integrated Innovation for Advancing the Indonesian Palm Oil Industry.” In his presentation, Dr. Ade reaffirmed BGA’s dedication to facilitating broader participation by Indonesian researchers in addressing practical challenges within the national palm oil industry.
“BGA operates primarily in upstream plantation management. Through this research grant initiative, we seek to explore the potential of Indonesian researchers in delivering applied solutions to key issues in the palm oil sector,” Dr. Ade stated.
Among the critical challenges highlighted were the decline in production capacity due to pest outbreaks and inefficiencies in the processing of crude palm oil into refined products. To address these issues, BGA is offering researchers access to plantation land, thereby providing an opportunity to apply their research’s findings.
Among the critical challenges highlighted were the decline in production capacity due to pest outbreaks and inefficiencies in the processing of crude palm oil into refined products. To address these issues, BGA is offering researchers access to plantation land, thereby providing an opportunity to apply their research’s findings.
In addition to faculty researchers, the 2025 Open Innovation Program is also open to university students across Indonesia. This initiative is expected to further promote research-based innovation originating from academic institutions such as the Faculty of Biology UGM, contributing meaningfully to the development of the national palm oil industry. Furthermore, it aligns with key objectives of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDGs No. 4 on Quality Education and SDGs No.17 on Partnerships for the Goals.
Through this initiative, PT BGA aspires to strengthen the integration between higher education institutions and industry, while fostering impactful and solution-oriented research in the fields of agriculture and plantation science in Indonesia.
Yogyakarta, February 20, 2025 – PT Bumitama Gunajaya Agro (BGA) continues to strengthen its commitment to driving innovation in Indonesia’s palm oil industry through its Open Innovation program. The socialization of this program was held at the Tropical Biology Auditorium of the Faculty of Biology, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), Yogyakarta, and was attended by both faculty members and students from the Faculty of Biology UGM. This event also marked the continuation of the collaboration between BGA and the Faculty of Biology UGM, which began last year.
In his opening remarks, Prof. Dr. Budi Setiadi Daryono, M.Agr.Sc., Dean of the Faculty of Biology UGM, emphasized the importance of cooperation between academic and industry to enhance the quality of research and innovation. He expressed great appreciation for the opportunity to continue this collaboration, especially since the Dean himself was one of the recipients of BGA’s innovation grant last year.
During the event, Dr. Ade Agung Laksono, Bumitama Academy Department Head at PT BGA, served as the keynote speaker. Under the theme “Integrated Innovation to Advance the Indonesian Palm Oil Industry,” Dr. Ade shared BGA’s commitment to opening opportunities for Indonesian researchers to directly contribute to the development and sustainability of the national palm oil industry. “BGA focuses on the upstream management of palm oil plantations, and through the research grant we offer, we aim to explore the potential of Indonesian researchers in providing practical solutions to the various challenges in the palm oil sector,” said Dr. Ade.
In his presentation, Dr. Ade also highlighted some of the main challenges facing the Indonesian palm oil industry this year, including reduced production capacity due to pest attacks and suboptimal processing of crude palm oil into edible oils. To address these issues, BGA is offering researchers the opportunity to apply their findings directly in the field, utilizing the land provided by BGA.
This year, the BGA research grant program not only invites faculty members but also opens up participation to students from universities across Indonesia. Through this initiative, it is hoped that the research innovations emerging from the Faculty of Biology UGM can further contribute to the advancement of the palm oil industry in Indonesia, while supporting the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly for inclusive education (SDG 4) and collaborative innovation (SDG 17). This initiative is expected to strengthen the synergy between education and industry, opening opportunities for more applicable research that can have a direct impact on the agricultural and palm oil plantation sectors in Indonesia.
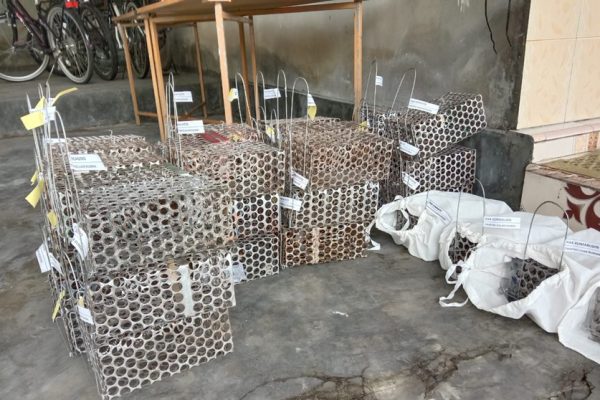
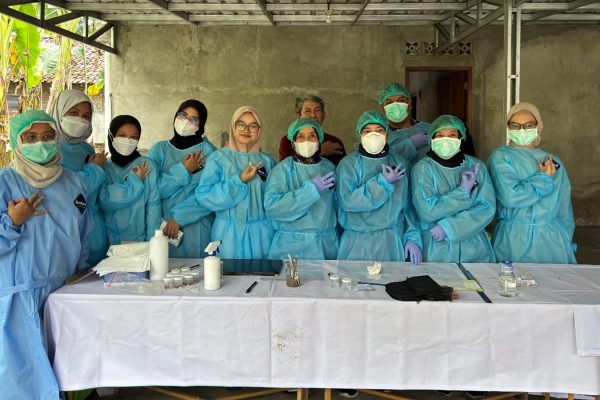
Bantul, Indonesia – February 19, 2025 – In a proactive public health initiative, students from the Faculty of Biology, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM) collaborated with the Bantul District Health Office and the Yogyakarta Public Health Laboratory Center (BBLABKESMAS) to conduct rodent surveillance in Beran Hamlet, Canden Village, Jetis Subdistrict, Bantul Regency. This joint effort was initiated following confirmed human cases of leptospirosis and hantavirus in the area, with the infections suspected to have also affected other family and community members.
The surveillance began on Tuesday, February 18, with the placement of 50 single-live rat traps. As a result, nine traps captured rats (Rattus spp.) and two traps captured Asian house shrews (Suncus murinus), both considered potential reservoirs of disease.
The student research team comprised Dita Dwi Putri, Zahwa Khoirun Nisa, Dhiyaa Sekar Hanum, Shaila Revita Zahra, and Trissa Amalia Putri and Rizky Nur Endah Sari. Their participation is part of the Merdeka Belajar Kampus Merdeka (MBKM) Research Program, supervised by Dr. Dra. Rr. Upiek Ngesti Wibawaning Astuti, B.Sc., DAP&E, M.Biomed.
Moving forward, molecular analysis will be conducted on the captured specimens to detect the presence of Leptospira bacteria and hantavirus, providing crucial data to inform future public health responses. This initiative reinforces the Faculty of Biology UGM’s dedication to community welfare and aligns with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including SDGs No 3: Good Health and Well-being, SDGs No 4: Quality Education, SDGs No 15: Life on Land, and SDGs No 17: Partnerships for the Goals.
The Faculty of Biology, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), in collaboration with Western Sydney University (WSU), successfully conducted the International Summer Course (ISC) program in Setulang Village and the Tane Olen Community Forest, Malinau Regency, North Kalimantan. This program followed a series of academic and cultural exchanges held earlier in Yogyakarta and Tarakan.
On Sunday, January 26, 2025, ISC participants arrived in Malinau and continued their journey to Setulang Village. The UGM delegation included two faculty members ; Dr. Rury Eprilurahman and Mukhlish Jamal Musa Holle, M.Env.Sc, D.Phil. and six students. The WSU delegation, consisting of two staff members, Dr. John Hunt and Louise Graham, and 16 students.
The program commenced with a warm welcome from the Setulang community, featuring traditional dance performances and remarks from the Village Head, Mr. Saleh Wang. Field activities began the following day with observations of rice fields and home gardens owned by local residents, including an introduction to farming system and the diversity of plant species cultivated in the Mr. Philius’s home garden, a village elder.
On January 28, the program moved to the Tane Olen Community Forest, a lowland dipterocarp forest known for its rich biodiversity. Participants traveled by pickup and continued on foot along river trails to two basecamps: Lepo Kalung and Waterfall Basecamp. From January 28 to February 5, daily activities included birdwatching, jungle trekking, herpetofauna observation (herping), and thematic discussions with local guides and researchers.
Dr. Rury Eprilurahman led herpetofauna identification sessions and delivered a herpetology sharing session on January 29. On January 30, local guides introduced participants to useful plant species during a trek through riparian and hilly zones. That evening, an ethnobotany discussion was held between ISC participants and the local community.
Dr. Rury Eprilurahman led herpetofauna identification sessions and delivered a herpetology sharing session on January 29. On January 30, local guides introduced participants to useful plant species during a trek through riparian and hilly zones. That evening, an ethnobotany discussion was held between ISC participants and the local community.
A key highlight took place on February 1 with a dialogue involving village elder Mr. Philius, Village Head Mr. Saleh Wang, and forest management representatives Andrew and Ran. The discussion focused on the history of Setulang, community conservation efforts, and sustainable forest management practices in Tane Olen.
The ISC program concluded on February 5 with a closing ceremony in Setulang Village. The event was attended by the Subdistrict Head of South Malinau Hilir, village officials, and community leaders, and featured traditional dance performances by residents of all ages.
This international collaboration not only enhanced cross-cultural academic exchange but also embodied the principles of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities), 14 (Life Below Water), and 15 (Life on Land).
Yogyakarta, 14 February 2025 – Faculty of Biology, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM) and Faculty of Science, Leiden University, celebrate a decade of academic and research partnership which has had a major impact on the development of biological science. Prof. dr. Herman Spaink from the Faculty of Science Leiden University, visits Faculty of Biology to celebrates their collaboration together with the Dean of the Faculty of Biology UGM, Prof. Dr. Budi Setiadi Daryono, M.Agr.Sc. and Vice Dean for Research, Community Service, Collaboration and Alumni Affairs, Dr. Eko Agus Suyono, M.App.Sc. along with Dr. Luthfi Nur Hidayat, S.Sc., M.Sc., lecturer at of Faculty of Biology as well as alumnus of Leiden University.
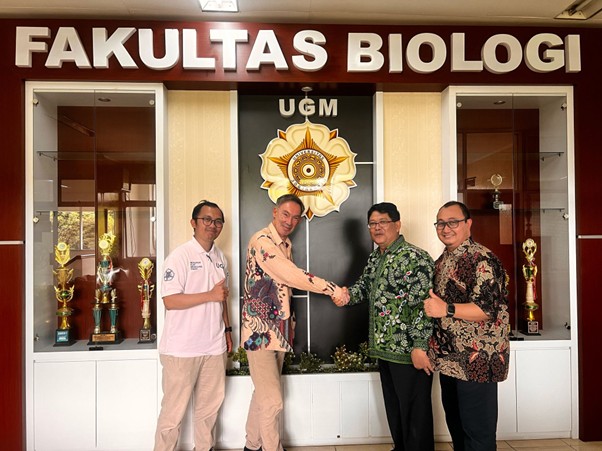

Since the collaboration began in 2015, Faculty of Biology UGM and Leiden University have carried out various joint research projects, student and lecturer exchange programs, as well as international scientific publications. Ultimately, in September 2024, Faculty of Biology UGM and the Graduate School, Faculty of Science, Leiden University signed a Joint Doctoral Degree Agreement. This program allows students from both universities to earn a doctoral degree with guidance from experts at both institutions. This agreement confirms the commitment of both institutions to strengthening academic and research relations in the field of biology.
Apart from that, the two universities also collaborated in establishing the Zebrafish Research Facility. This facility is expected to become an international research center to support the development of research in the health and natural products potential from Indonesia. This collaboration is in line with UGM’s vision of developing superior research in the fields of biotechnology and public health.
With a decade of success under their belt, both institutions are committed to continuing to expand the impact of research and innovation at the global level while strengthening their role as centers of excellence for biological research. It is hoped that this collaboration will continue to produce collaborative programs, student exchanges, joint research and quality scientific publications, providing significant benefits to the academic community and wider society.
This collaboration also contributes to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). In particular, SDG 4 (Quality Education) which supports access to quality education at the global level, SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) where the development of research facilities and scientific innovation in the field of biotechnology supports the progress of research infrastructure at the international level, and SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals) where collaboration between UGM and Leiden University reflects the importance of global partnerships in supporting research, innovation and academic development. Thus, this collaboration not only strengthens academic and research networks, but also contributes to achieving broader sustainable development goals.
Yogyakarta, 13 February 2024 – Faculty of Biology, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM) participated in discussions to initiate collaboration with University College Cork (UCC), Ireland. This discussion was led by the Secretary of the Directorate of Global Partnerships and Relations at UGM, Prof. Ir. Wiratni, S.T., M.T., Ph.D., IPM, and attended by delegates from various faculties at UGM, including the Faculty of Biology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences (MIPA), and Faculty of Agricultural Technology. The Faculty of Biology delegation was represented by Nur Indah Septriani, Ph.D., as Head of the International Affairs Office of the Faculty of Biology.
Ms. Neasa O’Connor, International Recruitment Manager College of Science, Engineering and Food Science UCC, conveyed the potential for collaboration between the UGM Faculty of Biology and the UCC School of Microbiology. On this occasion, UCC offers two master’s program schemes, regular and by research, as part of the initiation of a double degree program with the Biology Master’s program at UGM. Ms. Neasa highlighted the potential for double degree collaboration in the Master of Microbiome Science program, a new study program at UCC, as well as other master’s programs such as the Master in Bioinformatics and Master in Biotechnology and Industrial Sciences.
Nur Indah Septriani, Ph.D., expressed her appreciation and welcomed the initiation of collaboration with UCC. She mentioned that the Faculty of Biology UGM has established double degree collaborations with various world universities at undergraduate level through the International Undergraduate Program (IUP), as well as at master’s and doctoral levels. Apart from that, she also offers the potential for collaboration in annual international programs organized by the Faculty of Biology UGM, such as the International Summer Course (ISC) and the International Conference on Biological Science (ICBS).
This discussion is a strategic step in strengthening academic relations between the Faculty of Biology UGM and University College Cork, Ireland. The initiation of this collaboration is in line with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG 4) which aims to improve access and quality of higher education through international academic collaboration. Apart from that, this collaboration also supports SDG 17, which emphasizes the importance of partnerships between educational institutions in creating a positive impact on the development of science and human resources at the global level.