Arsip:
SDG 5 : Gender Equality
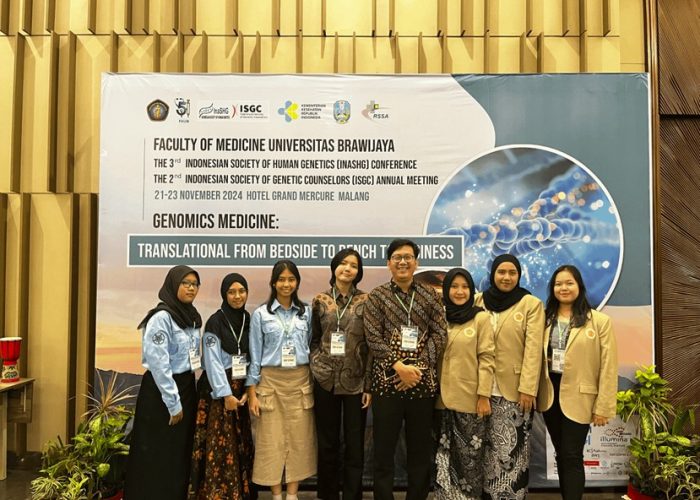
Undergraduate students from the Faculty of Biology at Gadjah Mada University—Alifia Nur Hidayah, Ardiza Puspa Rahmaningtyas, Farah Ayu Kamayani, Hana Magista Qathrunnada, Tazkia Mahsya Syavira, and Luisa Ramyahastri Paramatatya—participated in an international human genetics conference. This conference was the 3rd Indonesian Society of Human Genetics (InaSHG) Conference, held simultaneously with the 2nd Indonesian Society of Genetic Counselors (ISGC) Annual Meeting 2024. In collaboration with the Faculty of Medicine at Brawijaya University, the event took place from November 21-23, 2024, at the Grand Mercure Hotel, Malang. With the theme “Genomics Medicine: Translational from Bedside to Bench to Business,” the conference emphasized a comprehensive approach to the development of medical genetics. The program included research presentation sessions aimed at disseminating the latest research advancements, innovations in clinical practice, and developments in genetics policy. These sessions were designed to optimize knowledge exchange, strengthen interdisciplinary collaboration, and enhance the professional competence of participants. The conference also featured symposia with speakers from prominent national and international genetics experts.
During the event, students under the supervision of Prof. Dr. Niken Satuti Nur Handayani, M.Sc., and Indra Lesmana, S.Si., M.Sc., presented their research on the development of a Long-read Sequencing Application for Genotyping Hereditary Diseases in Humans. This research aims to develop an efficient genetic screening methodology for detecting various hereditary diseases, focusing on hemophilia A, obesity, thalassemia, and atopic dermatitis using long-read sequencing technology developed by Oxford Nanopore Technologies. The students gained valuable experience presenting their research at an international scientific forum, honed their scientific communication skills, and were inspired to further develop their research and broaden their knowledge about the latest advancements in genomics.
This research has significant implications, not only in academic contexts but also in supporting the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly Goal 3, which focuses on Good Health and Well-being. The contribution of this research to the development of genetics-based healthcare services represents a strategic step toward advancing the health system. The implementation of the developed technology is expected to have substantial impacts in several areas: optimizing preventive efforts and the management of genetic diseases, improving life expectancy for populations, and ensuring equitable, sustainable access to modern healthcare technologies.
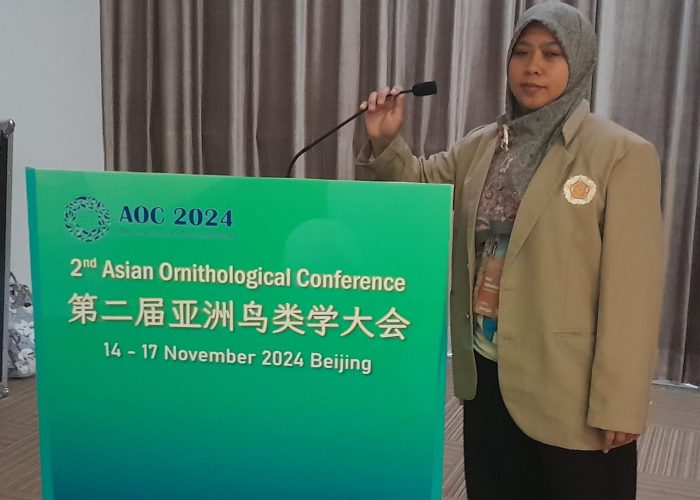
On November 14–17, 2024, the Asian Ornithological Conference (AOC) was held in Beijing, China, bringing together 528 delegates from 39 countries (505 from Asia and 23 from outside Asia). Attendees represented 76 universities, 37 research institutions, and 28 exhibitors, sponsors, and event supporters. This quadrennial conference, previously held virtually in Zhuhai, China, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, aims to foster academic exchange across Asia, promote ornithological research and conservation, and enhance the international status and influence of Asian ornithological organizations.
The vibrant conference was supported by the International Ornithology Union (IOU) and organized by the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with the International Zoological Society, China Ornithological Society, and the journal Avian Research. Over four days, the event facilitated knowledge-sharing on bird-related research across participating countries through plenary talks, symposia, and poster presentations.
Key conference highlights included:
- Plenary Talks: Eight speakers, including Indonesia’s Prof. Dr. Dewi M. Prawiradilaga from the National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN).
- Keynote Talks: Four speakers, with Indonesia represented by Mohammad Irham, M.Sc. (BRIN).
- Youth Talks: Three speakers from various countries.
- Symposia: 26 sessions with 190 delegates, including Indonesia’s Dr. Anik Budhi Dharmayanthi and Yohanna Dalimunthe, M.Si. (BRIN), Prof. Pramana Yuda (Universitas Atmajaya Yogyakarta), and Dwi Agustina (UGM graduate student and Program Coordinator at the Indonesian Cockatoo Conservation Association, KKI).
The conference also featured a bazaar of research tools and equipment, showcasing products from leading companies in China and beyond.
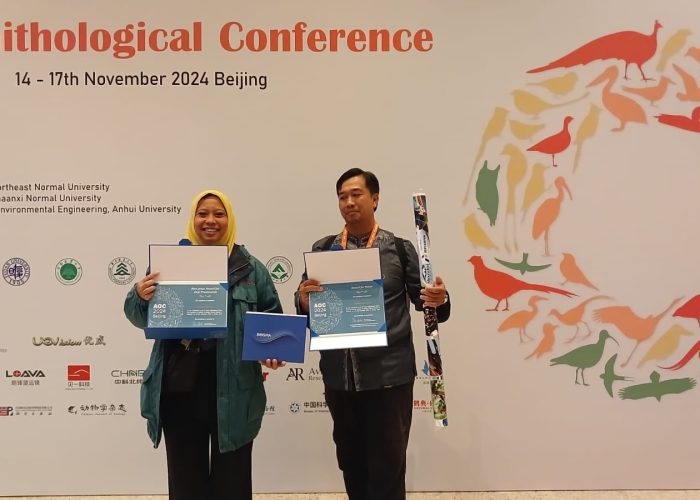
For UGM’s graduate students, Dudi Nandika and Dwi Agustina, attending the AOC provided invaluable opportunities to expand their networks, showcase their expertise, and gain broader insights into the global ornithological community. Both have extensive experience in bird conservation, particularly with parrot species, through their work at KKI.
Their participation was marked by exceptional achievements:
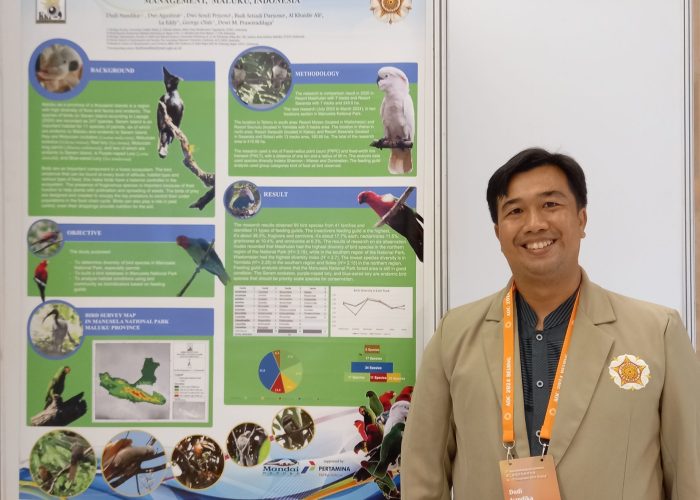
- Dudi Nandika received the First Prize Poster Award for his poster, “Recent Data Analysis on Feeding Guilds of Bird Communities as Bioindicators for the Management of Manusela National Park, Maluku.”
- Dwi Agustina earned the First Prize Presentation Award for her oral presentation, “Aligning Cockatoo Conservation Efforts with Local Huaulu Customary Wisdom on Seram Island, Maluku, Indonesia.”
Prof. Dr. Budi Setiadi Daryono, M.Agr.Sc., Dean of the Faculty of Biology at UGM and Dudi’s academic advisor, expressed his pride: “Alhamdulillah, congratulations on winning the awards for the best oral presentation and poster at the Asian Ornithological Conference. May this bring blessings and continued success.” Dr. Dwi Sendi Priyono, M.Si., their supervising lecturer, conveyed his congratulations and admiration for their achievements.
Dudi extended heartfelt gratitude, saying: “We are deeply thankful to Allah SWT, and to our mentors—Prof. Dr. Budi Setiadi Daryono, M.Agr.Sc.; Prof. Dewi Malia Prawiradilaga; Dr. Dwi Sendi Priyono, M.Si.; and George Olah, Ph.D.—for their invaluable guidance. Special thanks to the KKI team, colleagues Dr. La Eddy and Dr. Paulus from Universitas Pattimura, Dr. Herlina Agustin from Universitas Padjajaran, as well as friends and family who have always supported us.”
The achievements of Dudi and Dwi serve as a source of inspiration and a catalyst for further ornithological research and bird conservation efforts in Indonesia.
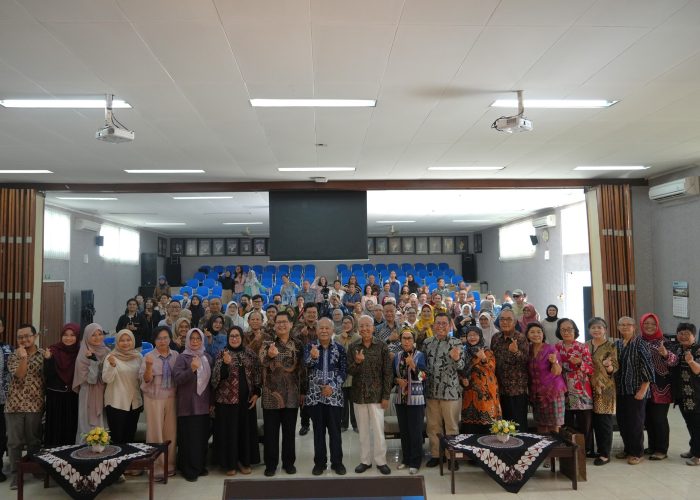
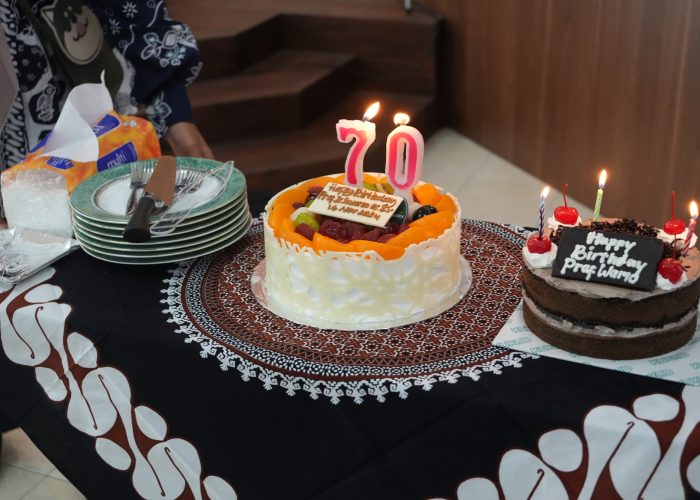
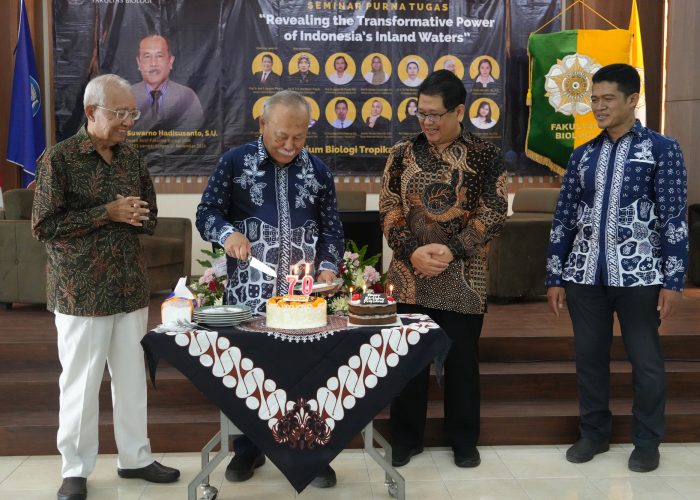
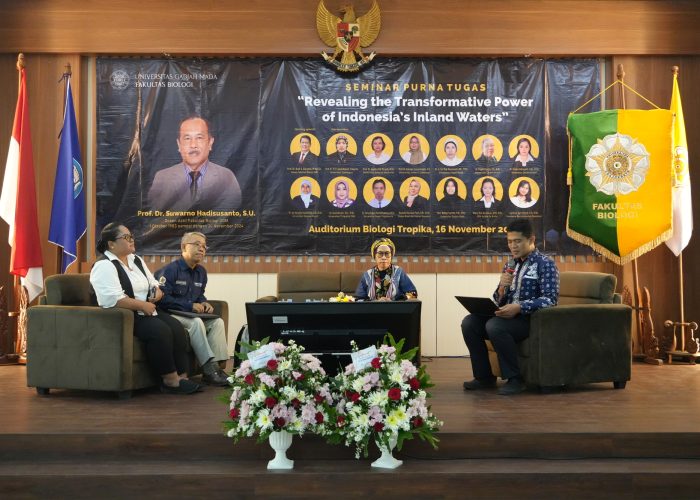
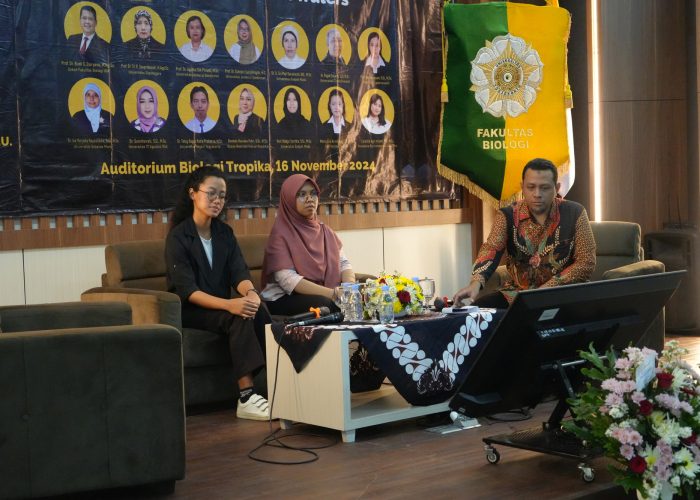
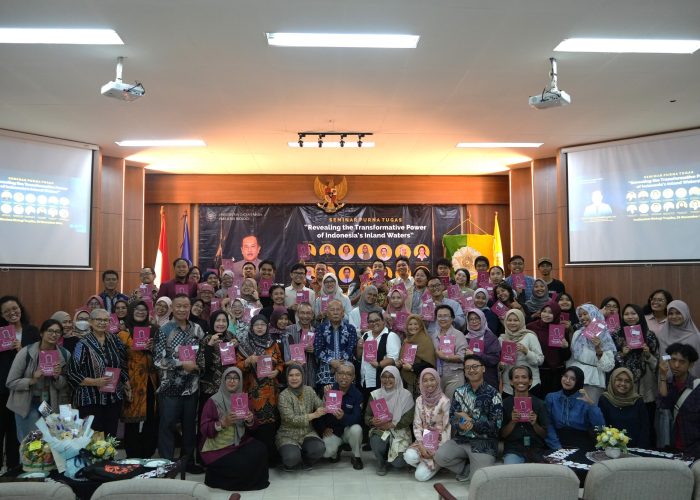
Yogyakarta, November 16, 2024 – The Faculty of Biology, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), hosted a Retirement Seminar titled “Revealing the Transformative Power of Indonesia’s Inland Waters” at the Faculty of Biology Auditorium. This event marked the retirement of Prof. Dr. Suwarno Hadisusanto, S.U., after 41 years of dedicated service as a lecturer. The seminar also coincided with Prof. Suwarno’s 70th birthday, making it a truly special occasion.
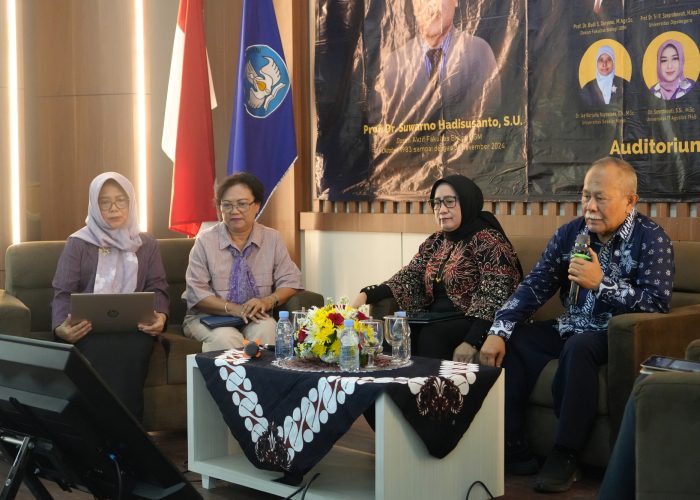
The seminar featured 13 distinguished speakers, all former students of Prof. Suwarno, representing various universities and research institutions. More than 170 participants from diverse backgrounds attended the event.
The opening remarks were delivered by the Chair of the Organizing Committee, Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Andhika Puspito Nugroho, S.Si., M.Si., who expressed deep gratitude for Prof. Suwarno’s dedication. “Prof. Suwarno has given us so much. We extend our heartfelt thanks and profound appreciation for his remarkable contributions,” he said.
The Dean of the Faculty of Biology, Prof. Dr. Budi S. Daryono, M.Agr.Sc., officially opened the event, stating, “The essence of this event is to honor Prof. Suwarno and convey our deepest gratitude, particularly from the Faculty of Biology UGM, for his dedication, commitment, and passion for his alma mater and the advancement of science.”
Following the remarks, attendees participated in a group photo session and were introduced to the new Biodiversity Curator Program—an innovative initiative supporting biodiversity conservation in Indonesia.
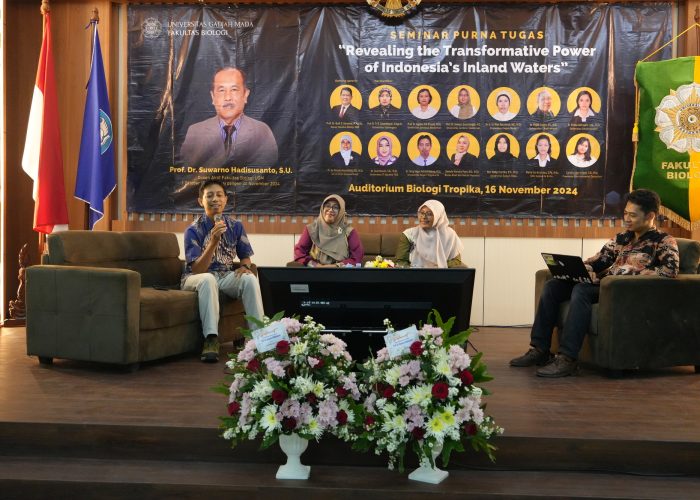
The seminar was divided into four sessions, each highlighting various aspects of Indonesia’s inland water potential and management challenges:
Session 1
Moderator: Siti Nurleily Marliana, Ph.D.
- Prof. Dr. Suwarno Hadisusanto, S.U. – The Variations and Multifunctions of Inland Waters
- Prof. Dr. Tri Retnaningsih Soeprobowati, M.App.Sc. (Universitas Diponegoro) – Paleolimnology for Sustainable Lake Management
- Prof. Dr. Agatha Sih Piranti, M.Sc. (Universitas Jenderal Soedirma) – Cultural Eutrophication of Lakes/Reservoirs and Mitigation Efforts
- Prof. Dr. Suhestri Suryaningsih, M.Si. (Universitas Jenderal Soedirman) – The Role of Watersheds in Supporting River and Lake/Reservoir Fish Populations
Session 2
Moderator: Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Andhika Puspito Nugroho, S.Si., M.Si.
- Dr. Ir. Sri Puji Saraswati, DIC., M.Sc. (UGM) – Eco-Hydrology of Aquatic Communities Amid Infrastructure Development
- Dr. Puguh Sujarta, S.Si., M.Si. (Universitas Cenderawasih) – Shallow Marine Conservation Culture
- Dr. Ervina Indrayani, S.Si., M.Si. (Universitas Cenderawasih) – Lake Sentani: Uniqueness and Richness of Its Biological Resources
Session 3
Moderator: Mukhlish Jamal Musa Holle, S.Si., M.Env.Sc., D.Phil.
- Dr. Ike Nurjuwita Nayasilana, S.Si., M.Si. (Universitas Sebelas Mare) – Water Conservation and Wildlife
- Dr. Susintowati, S.Si., M.Si. (Universitas 17 August 1945) – Serious Threats to Coastal Communities
- Dr. Tatag Bagus Putra Prakarsa, S.Si., M.Sc. (Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta) – Underground Waters: Supporting Life for Cave-Dwelling Bats
Session 4
Moderator: Dr. Rury Eprilurahman, M.Sc.
- Dwinda Mariska Putri, S.Si., M.Sc. (National Research and Innovation Agency) – Vertical Distribution of Zooplankton in Lake Laut Tawar
- Heni Wahyu Sartika, S.Si., M.Sc. (UGM) – Belik River as a Flowing Water Management Model During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Maria Eva Kristiyani, S.Si., M.Sc. (De Britto College High School) – Coastal Waters for Aquaculture
- Carolina A. Inlandia, S.Si., M.Sc. (Environmental Consultant) – Water Pollution Potential and Management of Tambakboyo Reservoir, Sleman
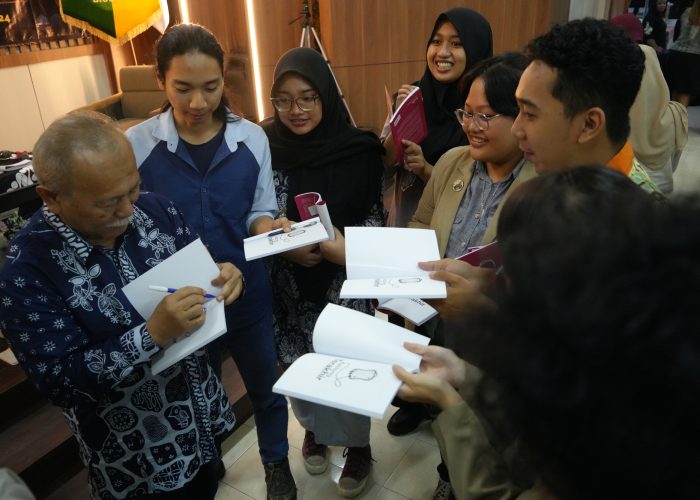
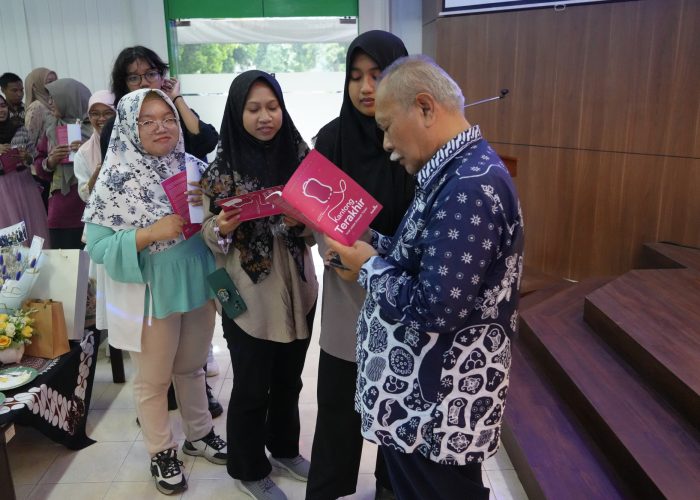
To conclude the event, Prof. Suwarno generously distributed 70 copies of his book, “Kantong Terakhir Anak Adalah Amanah Tuhan” to participants.
The attendees extended their prayers and best wishes to Prof. Dr. Suwarno Hadisusanto, S.U., for his extraordinary dedication over the past 41 years. They wished him health, happiness, and blessings in his retirement. His legacy of knowledge and inspiration is expected to drive progress for future generations.
Thank you, Prof. Suwarno, for being a role model for us all.
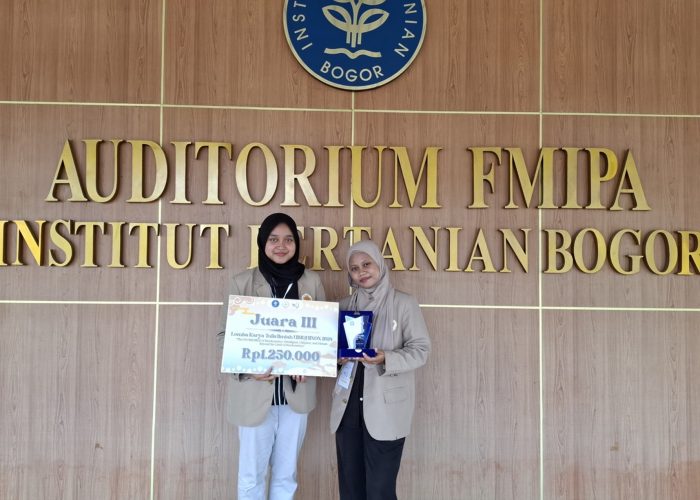
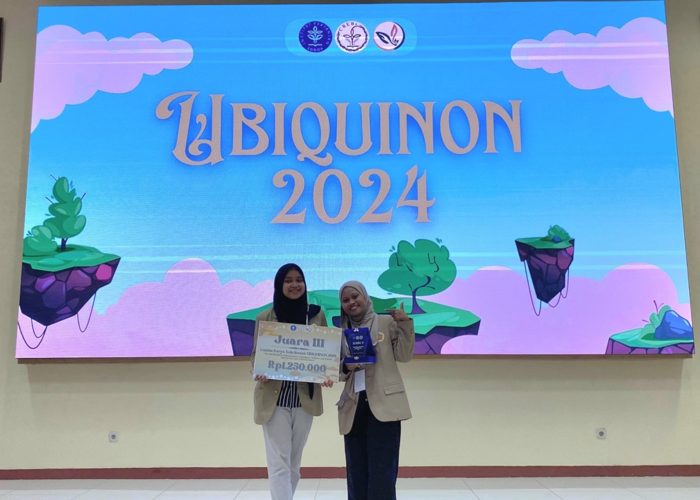
Students from the Faculty of Biology, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), achieved a remarkable achievement by winning third place in the UBIQUINON 2024 Scientific Writing Competition. This prestigious event, themed “The INCREDIBLE of Biochemistry: INtelligent, CREative, and DIstant Beyond the Limit of Biochemistry,” was organized by the Community of Research and Education in Biochemistry (CREBs) at Institut Pertanian Bogor (IPB) on September 21–22, 2024.
The UGM team, consisting of Nisa Abidah and Almas Lathifatul Ula, class of 2021, presented their scientific work titled “Future Therapeutic Development Based on Mutation Trend Analysis and Design of Antibiotic Resistance Detection to Prevent the Superbug Gonorrhea Phenomenon.” The research, supervised by Tyas Ikhsan Hikmawan, S.Si., M.S., Ph.D., addresses the critical challenge of antibiotic resistance, focused on gonorrhea, one of the most dangerous superbugs. The study proposes innovative future solutions through the development of diagnostic tools for detecting antibiotic resistance.
UBIQUINON 2024 aimed to enhance understanding of biochemistry’s pivotal role as a foundational science for numerous applied disciplines. The event consisted of two main segments: Competitions in three categories—Scientific Writing, Essay, and Infographics and UBITALK, a seminar discussing cutting-edge issues in applied biochemistry.
The competition attracted dozens of submissions, with only 15 finalists selected from leading universities across Indonesia, including Universitas Indonesia (UI), Institut Teknologi Bandung (ITB), Universitas Sebelas Maret (UNS), Institut Pertanian Bogor (IPB), Universitas Hang Tuah, and Universitas Diponegoro (UNDIP).
The competition attracted dozens of submissions, with only 15 finalists selected from leading universities across Indonesia, including Universitas Indonesia (UI), Institut Teknologi Bandung (ITB), Universitas Sebelas Maret (UNS), Institut Pertanian Bogor (IPB), Universitas Hang Tuah, and Universitas Diponegoro (UNDIP).
The overarching theme of UBIQUINON 2024 explored sub themes such as Renewable Energy Applications, Biotechnology, and Medicine. The UGM team’s work fell under the medical subtheme, showcasing a groundbreaking approach to combating antibiotic resistance.
This achievement highlights not only the innovative capacity of UGM’s Faculty of Biology students but also their commitment to advancing impactful scientific knowledge, particularly in addressing global health challenges. The success reinforces UGM’s dedication to supporting the realization of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly in promoting health and fostering sustainable scientific advancements.
[Author: Nisa Abidah]
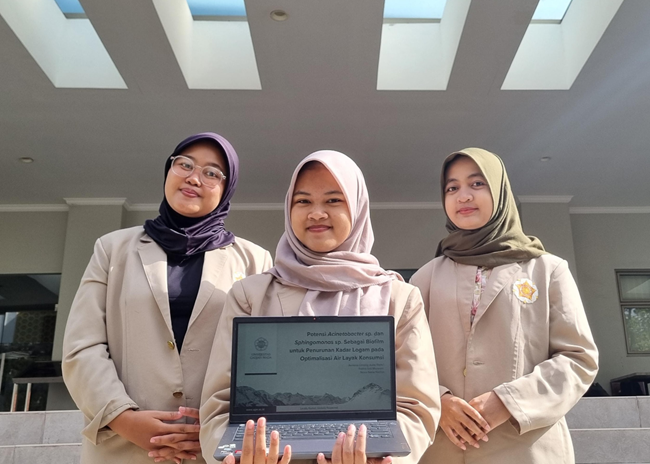
A student team from the Faculty of Biology, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), class of 2022, under the guidance of Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Andhika Puspito Nugroho, S.Si., M.Si., achieved a remarkable achievement at the 2024 Science Event (SCEVENT) Essay Competition organized by the Scientific Reasoning Student Unit (UKM Penalaran) of Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember.
During the final presentation on Sunday, October 27, 2024, The OTW team, led by Avriena Lintang Aulia Riefa’i and team members Fatiha Esti Murwani and Nova Nana Nadiya, presented “The Potential of Acinetobacter sp. and Sphingomonas sp. Biofilms for Reducing Metal Contaminants in Optimizing Potable Water Quality.” The essay addressed the poor quality of drinking water due to metal contaminants such as iron (Fe) and manganese (Mn), that lead to metallic tastes and odors in drinking water. Beyond discomfort, these contaminants pose health risks if present in concentrations exceeding safe limits. The team proposed an innovative solution by utilizing biofilms formed by metal-oxidizing bacteria, Acinetobacter sp. and Sphingomonas sp., as bioremediation agents by modifying water filtration systems in wastewater treatment plants (WWTP) to optimize the filtration process.
With this concept, the OTW team developed a biofilm-mediated bioremediation system for domestic applications. Their innovative approach earned them first place, triumphing over 47 competing teams.This outstanding achievement inspires other students to continually develop creative ideas and practical solutions to address diverse challenges, thereby contributing to support the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The OTW team aspires for their innovation to lay the groundwork for future advancements in potable water filtration methods, specifically through microbial biofilm utilization. Aligned with SDG Goal 6, “Clean Water and Sanitation for All,” this initiative underscores the importance of ensuring the availability and sustainable management of clean water for everyone.
[Author: Fatiha Esti Murwani]
On Saturday, September 28, 2024, the Marine Study Group (KSK) of the Faculty of Biology Universitas Gadjah Mada organized the Kopdar Alumni 2024, themed “Developing Career and Further Study Plans.” This event took place at the Auditorium of the Faculty of Biology, UGM, attended by KSK Biogama members from various cohorts.
The speakers featured in this event were Basith Kuncoro Adji, S.Si., M.Sc. from the University of Birmingham, and Muhammad Arief Budhiman, S.Si. from Pertamina Foundation. They shared insights regarding their experiences after graduation, discussing topics related to further studies and career paths in environmentally focused industries. Their presentations included information on study pathways, career opportunities, and essential skills for Biology students.
The event involved guided group discussions organized by the committee. Participants were divided into small groups to create mind maps regarding their career or further study plans. These mind maps were required to encompass information on the skills needed, career objectives, and strategies to achieve them. This group discussion lasted for 30 minutes, during which participants actively exchanged ideas and visualized their thoughts through mind mapping.
Following the group discussions, each group presented their mind maps to the speakers and the audience. The speakers provided feedback and suggestions regarding the steps that could be taken to achieve their planned career or further study goals.
The event concluded with the presentation of mementos to the speakers in appreciation of their participation and the knowledge they shared, followed by a group photo session with all participants, both in-person and online.
The event concluded with the presentation of mementos to the speakers in appreciation of their participation and the knowledge they shared, followed by a group photo session with all participants, both in-person and online.
[Author: KSK]
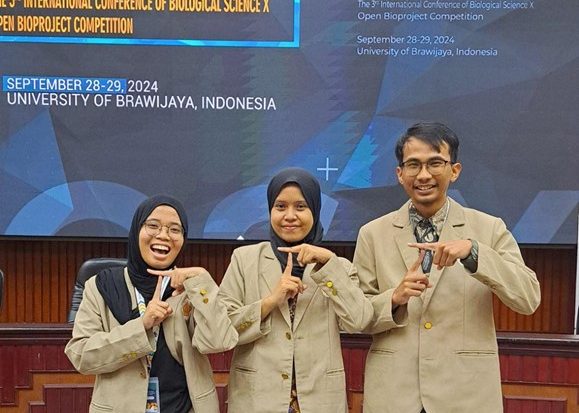
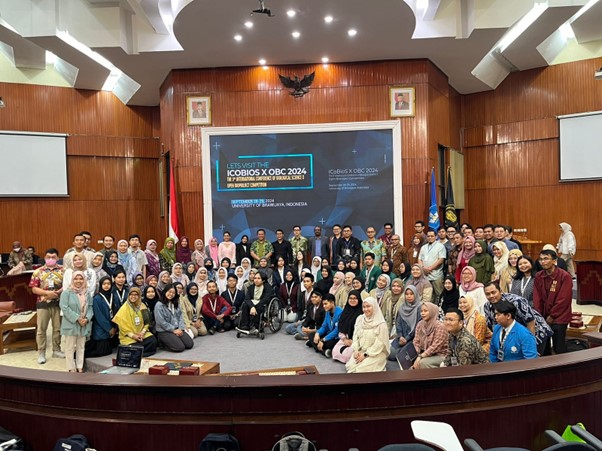
Biology students at Universitas Gadjah Mada made another achievement by winning a silver medal at the 3rd International Conference of Biological Sciences (ICoBioS) 2024. The conference, held by Universitas Brawijaya on September 27-28, 2024, had the theme “Recent Update in Bioinformatics, Synthetic Biology, and Nanobio Science for Better Future.” This success strengthens UGM’s standing in the international scientific community, particularly in driving innovation and progress in modern biological sciences. This achievement was achieved by Thoriq Abdul Halim, Tiara Putria Judith, and Salfa Athallah Agtari Nabillah students from the 2021 cohort, under the guidance of Dr. Ganies Riza Aristya, S.Si., M.Sc., Ph.D., presented research titled “Comparative Analysis of DNA Barcodes Based on Nuclear and Chloroplast Genes for Phylogenetic Reconstruction of Sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) in Java Island.”
In their presentation, the team discussed the importance of sugarcane (S. officinarum L.) production, which contributes to 80% of global sugar production. Despite Java Island supplying 61% of the national output, Indonesia only produced 2.23 million tons of sugar in 2019, while imports reached 5.46 million tons in 2021, mainly from Thailand. The low sugarcane yield is due to the narrowing of genetic diversity caused by domestication. Given the complexity of the genome and the difficulty in distinguishing morphological characteristics, the team utilized DNA barcoding techniques to analyze genetic variation in nuclear DNA and chloroplast DNA of sugarcane. This research aims to identify intra- and interspecific genetic variation among sugarcane cultivars as part of efforts to improve varietal identification, agricultural productivity, and food security in Indonesia.
The theme and goals of this research align with UGM’s commitment to supporting the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDGs No.2 on ending hunger and enhancing food security, and SDGs No.12, which focuses on sustainable production and consumption through efforts to increase sugarcane productivity and reduce dependence on sugar imports in Indonesia.
On Friday, October 11, 2024, the Faculty of Biology at Gadjah Mada University (UGM) held the third day of Biocapture (Biology Career Preparation for the Future) in the Tropical Biology Auditorium. The event commenced at 1:30 PM, guided by Feliciana Clara Henderison as moderator.
The first session, “Leaderless Group Discussion,” featured Arief Pratomo Manunggal as the speaker. This session discusses critical and analytical thinking, leadership, communication, teamwork, problem-solving, and decision-making. The session concludes by awarding certificates and mementos to the speaker.
The second session featured reflections and feedback from the participants and concluded with closing remarks delivered by the Deputy Chair of Biocapture 2024, Ganies Riza Aristya, S.Si., M.Sc., Ph.D.
On Thursday, October 10, 2024, the Faculty of Biology at Gadjah Mada University (UGM) held the second day of Biocapture (Biology Career Preparation for the Future) in the Tropical Biology Auditorium. The event commenced at 1:30 PM, guided by Soen Eliora Valerie Natania as moderator.
The first session, “How to Kick Off Your First Interview,” featured Susana Nur Kusumaningsing as the speaker. This session addressed key preparations required before attending a job interview, encompassing aspects from mindset to appropriate attire. It also provided insights into the interview process from recruiters’ perspectives, enabling participants to better understand their expectations.
The second session, facilitated by Chandra Gupyta, continued the discussion from the previous day on “CV Lab: Tailoring Your Profile for Every Opportunity.” This session featured practical simulations, where participants were required to bring their pre-prepared CVs. Participants then organized into pairs to peer review each other’s CVs. This activity allowed participants to discern the strengths and areas for improvement in their CVs and offered constructive feedback for enhancement.