The Averin team (Antivenom use Tamarind) from UGM discovered the potential of tamarind seeds (Tamarindus indica) as an alternative treatment for ground snake (Calloselasma rhodostoma) bites. This research was conducted by Oktaviani Nisa Hanafiah (Veterinary Medicine), Fauzela Azira Ainaya (Biology), Fani Nur Maftukhah (Pharmacy), Rahmadina Nur Azizah (Pharmacy), and Khansa Fortuna Putri (Veterinary Medicine). The research was funded by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Research, and Technology (Kemendikbudristek) and Universitas Gadjah Mada. It hoped that this support will help address the issues of access and cost of snake bite treatment.
“This research aims to provide a theoretical foundation and preclinical data on the effectiveness of T. indica seed extract against C. rhodostoma snake bites. The results of this study could contribute to alternative treatments, reducing mortality rates from C. rhodostoma bites in Indonesia,” said Oktaviani.
Oktaviani emphasized the importance and urgency of this research. “According to WHO data, Indonesia experiences around 135,000 snake bite cases annually, with a mortality rate of 5-10%. The C. rhodostoma snake is a significant cause of death in Java. However, the Antivenom Serum (SABU) for these snake bites is not widely available and remains expensive,” Oktaviani added.
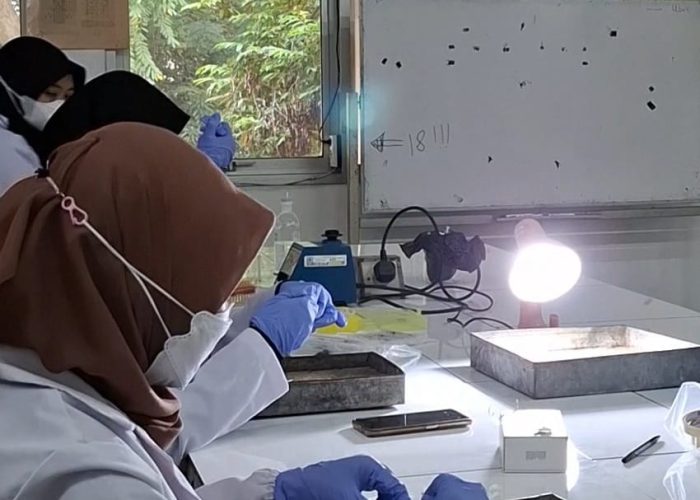
The tamarind seed extract was tested in vivo against C. rhodostoma venom, showing that in the group treated with tamarind seed extract, the hemorrhagic area was significantly smaller compared to the group treated with snake venom alone. Therefore, T. indica shows promise as a new treatment for snake bites, especially for C. rhodostoma. Our dedication to this research drives us to continue exploring nature’s potential to enhance human life, Oktaviani stated. These findings were presented at the National Seminar on Tropical Biology (SNBT) on July 20, 2024. [Author: Fauzela Azira Ainaya]