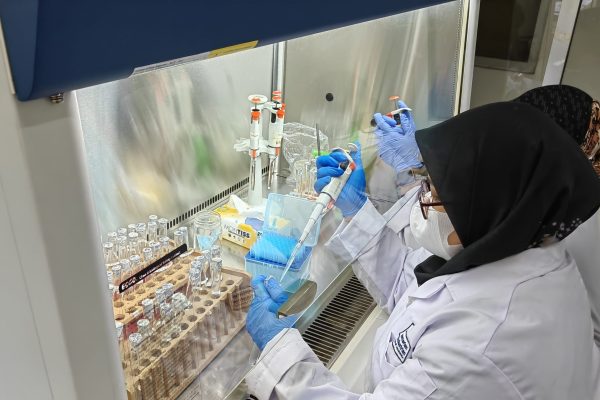
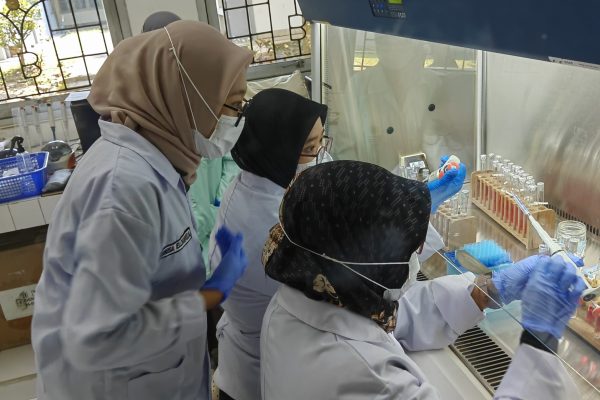
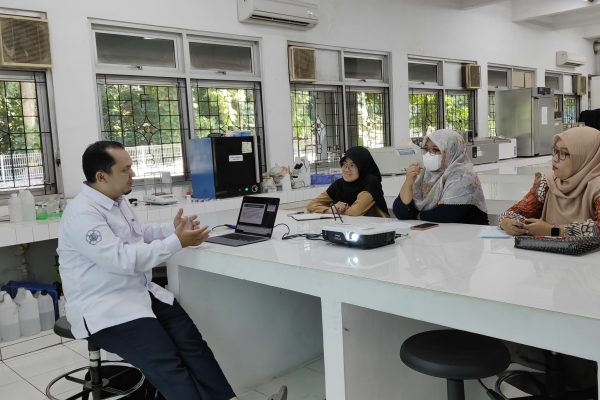
SDG 3 : Establish Good Health and Well-Being
Pathogen Molecular Biology
Malaria and Vector Resistance
Pathobiology of Emerging and Vector-borne Diseases
Human Genetic Diversity and Diseases
Structural Biology and Cell Signaling
SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being): advancing infectious disease research and developing genomics-based health solutions.
SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure): enhancing multi-omics research infrastructure and scientific collaboration.
SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals): strengthening national research networks in molecular biology and health.
- The dynamics of the cardiomyocyte transcriptome and chromatin landscape: Her team mapped out the changing gene expression patterns and chromatin architecture throughout heart development, revealing the timing and regulation of key developmental processes.
- Insights into the pacemaker system: By profiling the transcriptome of the sinoatrial ring—the zebrafish heart’s natural pacemaker—Dr. Winata uncovered both conserved and novel genetic programs, highlighting parallels with human heart rhythm regulation.
- Molecular blueprint of the secondary pacemaker: Genomic and physiological analyses of the atrioventricular canal exposed the genetic framework that defines this lesser-known pacemaker region, providing new understanding of how rhythmic contractions are coordinated.
- The role of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs): Dr. Winata underscored the importance of SNPs in shaping individual susceptibility to congenital heart defects and arrhythmias, underlining the potential of personalized medicine.
The lecture concluded with an open invitation from Dr. Winata to collaborate. She expressed keen interest in working with researchers and students from the Faculty of Biology and welcomed those interested in joining her lab in Warsaw to explore zebrafish-based research further.
This event not only deepened understanding of heart development but also laid the groundwork for international research collaboration, reinforcing the Faculty’s commitment to advancing biomedical science through global partnerships.

A Strong Scientific Foundation
Choosing UGM
Adapting to a New Environment
Daily Life and Culinary Discoveries
Passion for Parasitology
Wellbeing and Community
Looking Ahead
Nuclear Energy Research Organization – BRIN
Tuesday, July 29, 2025 | Auditorium Building 720, BJ Habibie Science and Technology Area, BRIN Serpong