Arsip:
SDG 4 : Provide Quality Education
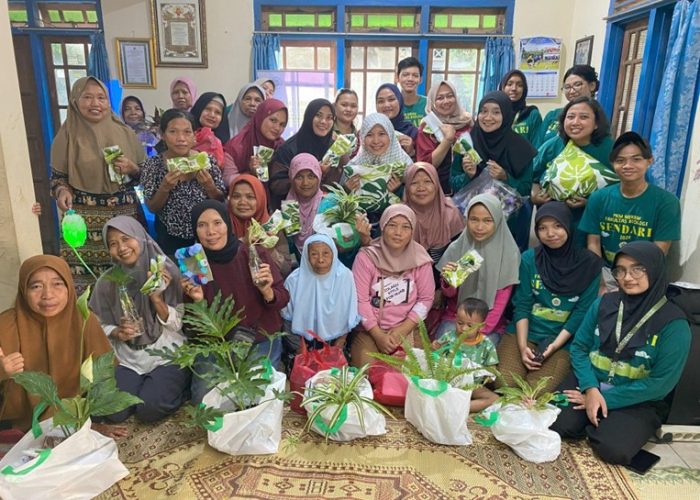
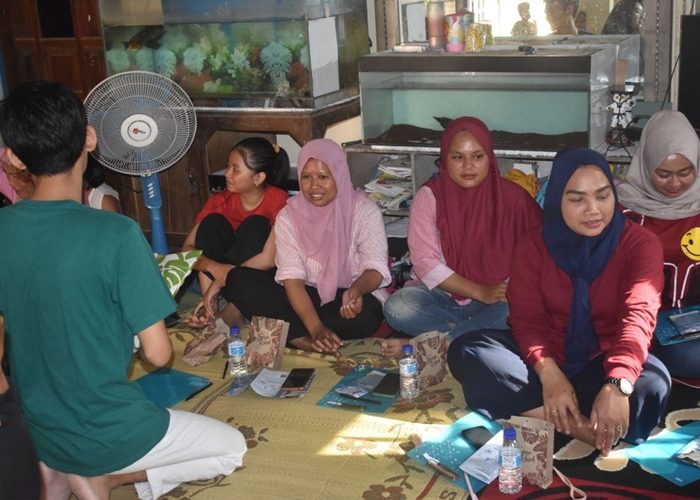
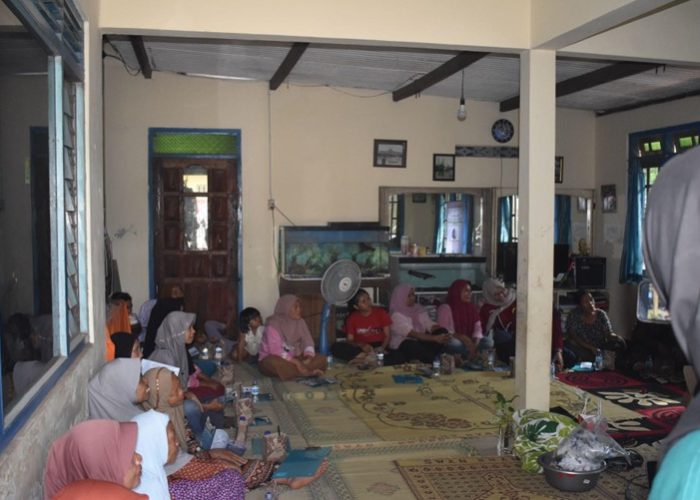
Yogyakarta, October 26, 2024 – The Community Service Team of the Merdeka Belajar Kampus Merdeka (PkM-MBKM) Program from the 2024 Biology Study Program conducted a community service activity titled “Processing Inorganic Waste and Combating Air Pollution Using Plants” on Saturday, October 26, 2024. Guided by supervising lecturer Mrs. Novita Yustinadiar, S.Si., M.Si., this event aimed to raise community awareness of sustainable inorganic waste management and the utilization of plants to reduce air pollution caused by waste incineration and motor vehicle emissions.
The event began at 2:00 PM WIB with an opening address from Mrs. Novita Yustinadiar, S.Si., M.Si., followed by the main presentation delivered by Aisyah Balqis Febriana. In her session, Aisyah explained that inorganic waste such as plastic, bottles, paper, and cardboard can be sorted and sent to waste banks for recycling, thereby enhancing their utility. Additionally, the concept of waste-to-energy was introduced, specifically the use of waste combustion heat as an environmentally friendly source of electricity, similar to Japan’s use of incineration technology. However, this technology is not yet feasible in Indonesia due to technological limitations. Currently, many people resort to burning waste to eliminate it, which has negative consequences for the environment, health, and society. One example discussed in the session was the production of microplastics from waste burning, which can contaminate soil, water, and air, posing risks to human, animal, and plant health. Thus, raising awareness about the dangers of waste burning and exploring alternative solutions for inorganic waste management is essential. In addition to recycling through waste banks, other potential solutions for managing inorganic waste include creating crafts and upcycling waste into valuable and marketable items. The session also covered air pollution mitigation using plants, including types of plants that absorb air pollution and the mechanisms by which plants reduce pollutants.
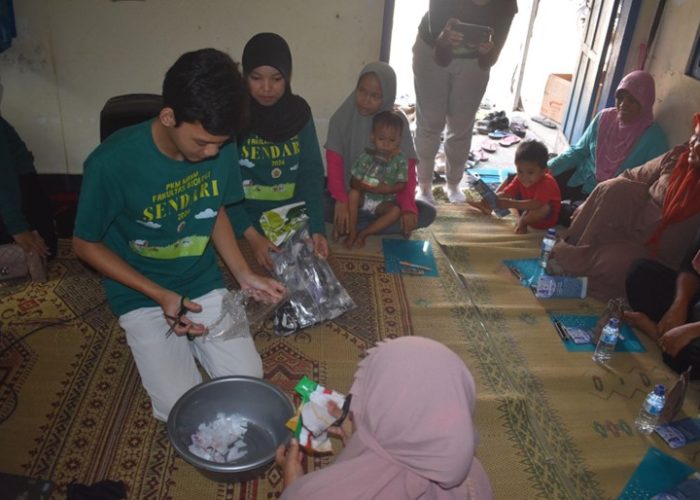
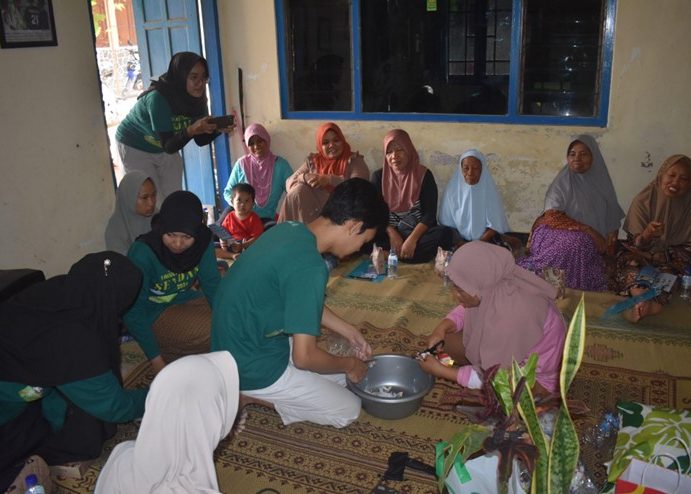
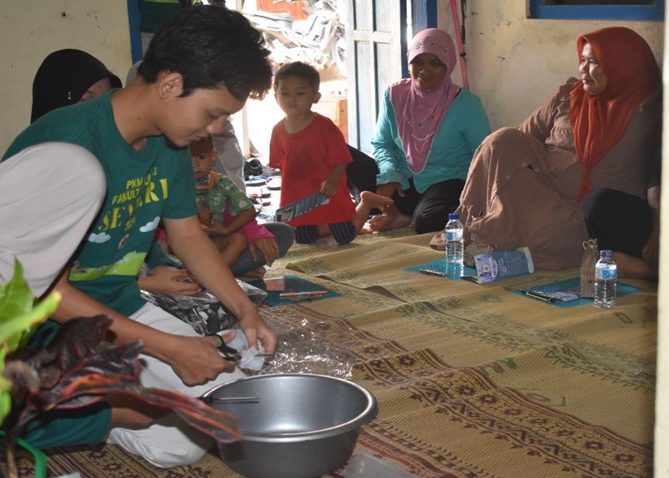
Following the presentation, Wisnu Prabowo conducted a hands-on demonstration, showing participants how to make sofa cushions filled with clean, recycled plastic, followed by the distribution of cushion covers and plastic zip covers to all attendees. Then, Ardiah Pramesti Cahyani presented a tutorial video along with a display of creative items made by the student team, such as lanterns from plastic spoons, flowers from plastic bags, flowers from used plastic bottles, frames from bottle caps, flower pots from bottles, and glass bottle vases for water propagation. These creations served as daily-life inspirations for repurposing inorganic waste.
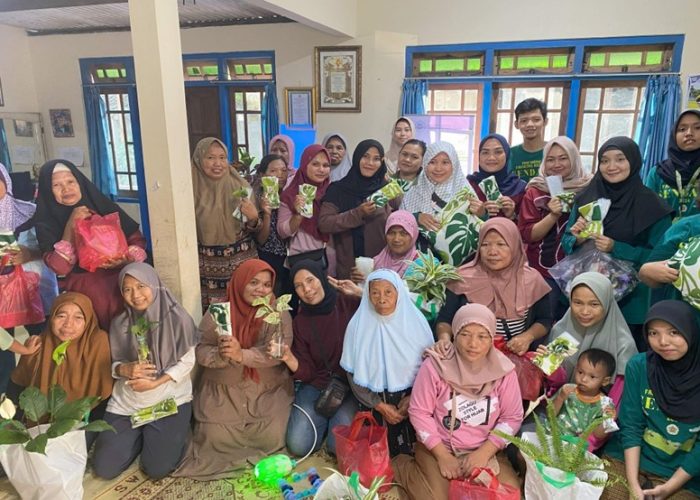
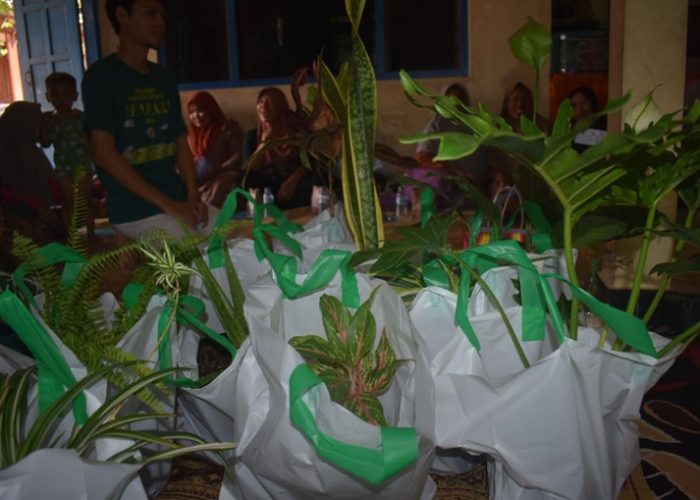
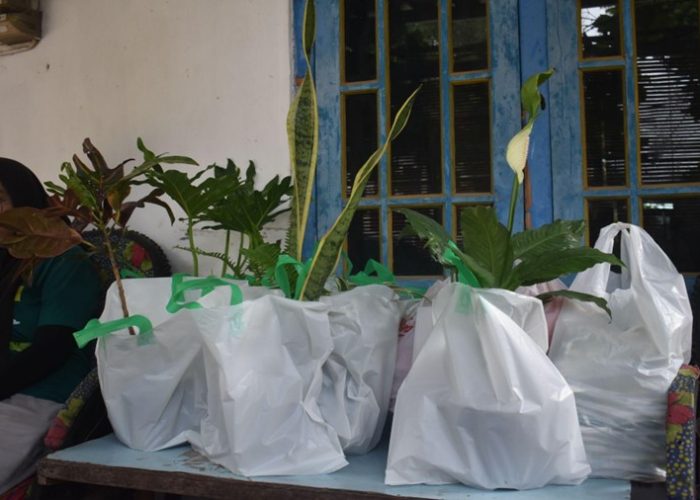
Participants engaged in a Q&A session and took a post-test to assess their understanding of the material. Attractive door prizes, including air-purifying houseplants and other gifts, were awarded to participants who actively engaged in the discussion. The event concluded with a recap video of the PkM-MBKM 2024 program, highlighting the series of environmental education activities.
The program closed with a farewell from Mrs. Novita, a group photo session with all participants and the team, and the distribution of souvenirs as tokens of appreciation. This community service program, which concluded at 4:00 PM WIB, is hoped to provide the community with new insights on environmental preservation through waste management and plant use as a solution for air pollution mitigation. We extend our gratitude to the Faculty of Biology for funding this event through the 2024 PKM-MBKM Grant, hoping it will continue to benefit the broader community.
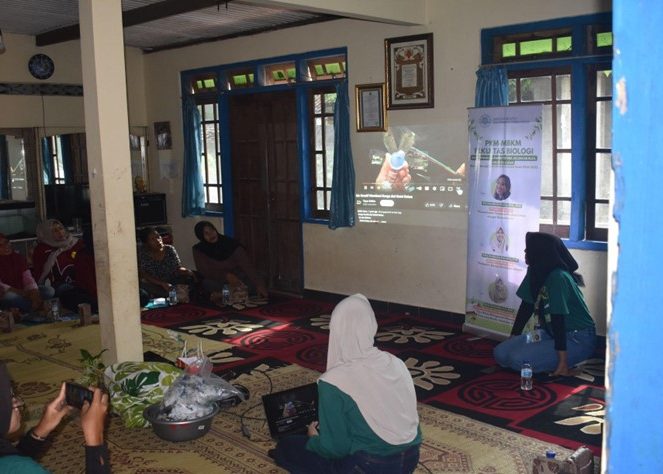
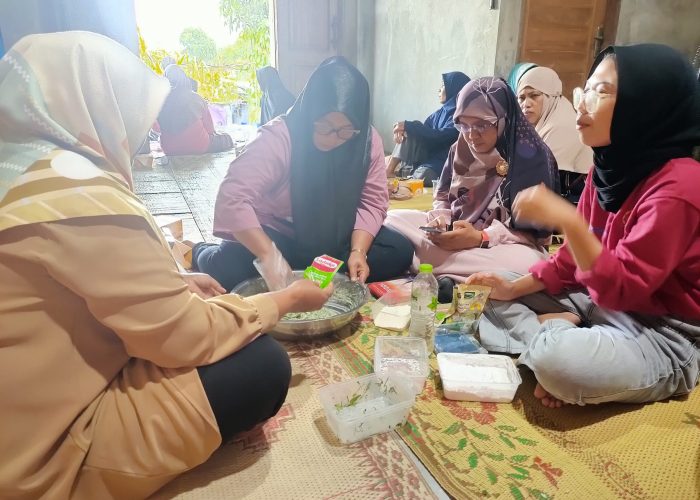
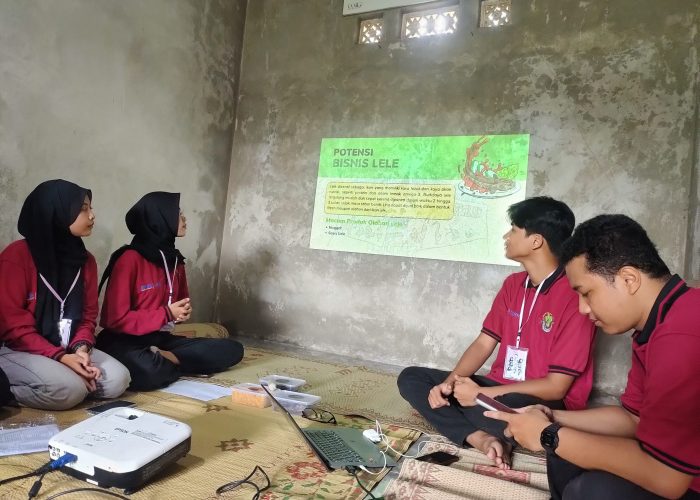
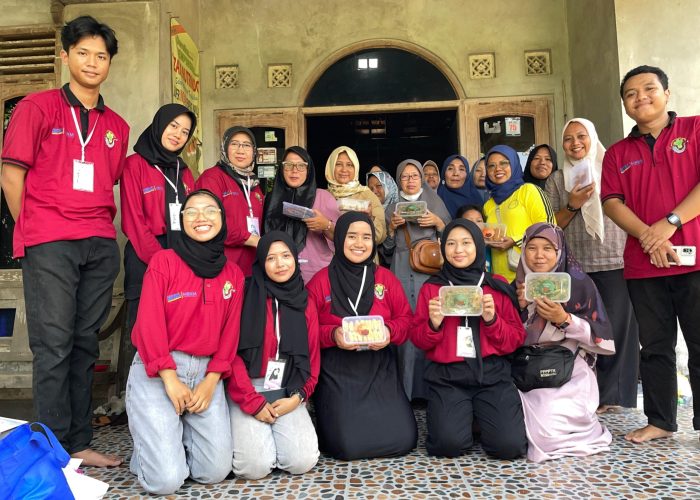
The PkM-MBKM Program of the Faculty of Biology UGM, led by Prof. Diah Rachmawati, S.Si., M.Si., in collaboration with the Kelompok Wanita Tani (KWT) Amanda in Kepuh Wetan, Wirokerten, Banguntapan District, Bantul Regency, Special Region of Yogyakarta, held a circular waste management training event based on aquaponic technology and catfish farming on Sunday, October 27, 2024, from 08.30 to 11.30 AM. The PkM-MBKM team, comprising members Hanif Fauzan Saputra, Salma Nur Majidah, Maharani Pratiwi S.A., M. Reza Hendriansah, Rima Vegi Santika, Eka Nur Oktavia, Adzkiya Aqmaliza R., and Agra Daffa Putra, presented strategies for product processing and marketing, followed by a demonstration of processing techniques for products made from catfish and water spinach to maximize the added value of aquaponics.
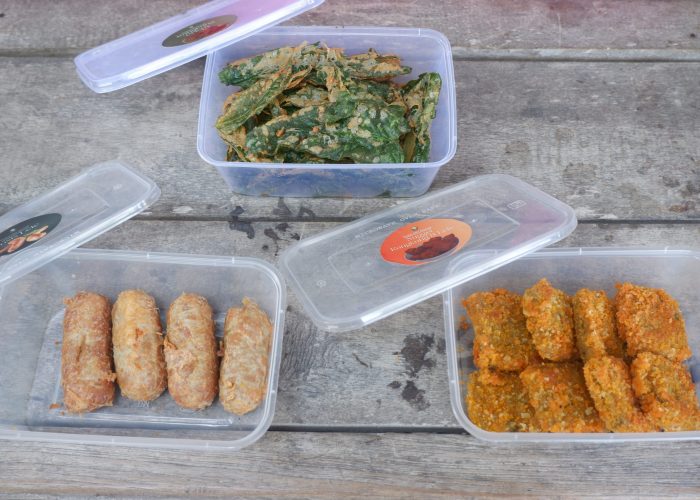
The activity began with an introduction to the business potential of catfish and water spinach, both rich in nutrients and protein. With innovations turning these ingredients into various products, such as catfish nuggets, catfish sausages, and crispy water spinach, it is hoped that these could serve as new business opportunities for KWT Amanda. Product innovation aims to expand the market by offering a variety of healthy and nutritious local food options. In addition to product innovation, choosing of safe, efficient, and attractive packaging design is also crucial. With engaging and informative packaging, these products are expected to attract consumer interest. To support sales, the PkM-MBKM team also provided an introduction to branding and digital marketing strategies by explaining how to use social media to educate participants on effective digital marketing techniques, from understanding target consumers to utilizing social media platforms for promotion. Marketing via social media is seen as a vital factor in increasing sales and building brand awareness.
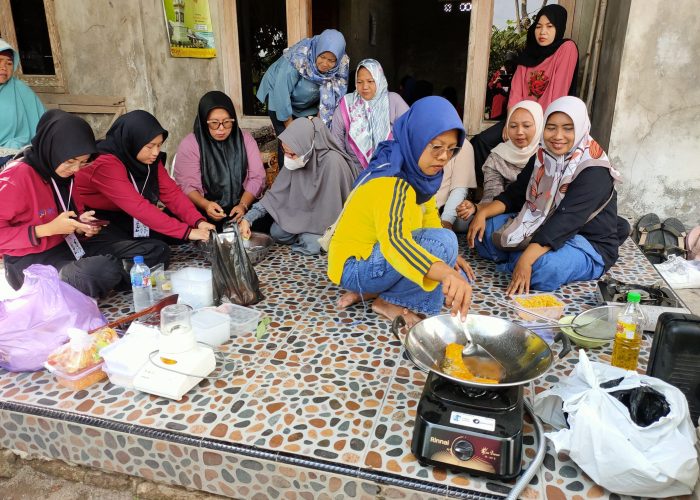
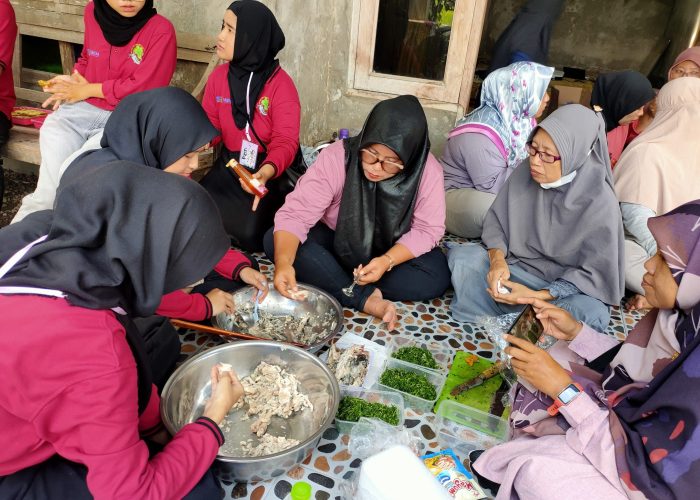
The next activity involved a product processing demonstration using aquaponics product, namely catfish and water spinach. The PkM-MBKM team provided hands-on training for KWT Amanda members on how to process catfish and water spinach into three high-value products: catfish nuggets with water spinach, crispy water spinach, and catfish sausage. During the demonstration, the KWT Amanda participants showed great enthusiasm in following each stage of product preparation, from ingredient preparation to cooking, resulting in quality products ready for the market. They paid close attention to the cooking process and actively asked questions to ensure optimal quality. After the cooking session, participants enjoyed the processed products, such as catfish nuggets with water spinach, crispy water spinach, and catfish sausages, which were delicious and had a desirable texture. KWT Amanda members also felt inspired after seeing the variations of catfish processed into different forms, such as catfish nuggets with water spinach and catfish sausage, which are more appealing to children. These processed products provide a solution for supplying high-quality protein and fiber to families, especially for children needing balanced nutrition during growth, thus fulfilling nutritional needs and ensuring a healthy life (SDG 3).
The socialization and training activities for processing aquaponics product can provide new ideas for processing to increase family income from aquaponics (SDG 4 and 8). The successful collaboration also strengthens sustainable relations between the PkM-MBKM Faculty of Biology UGM and its partners (SDG 17).
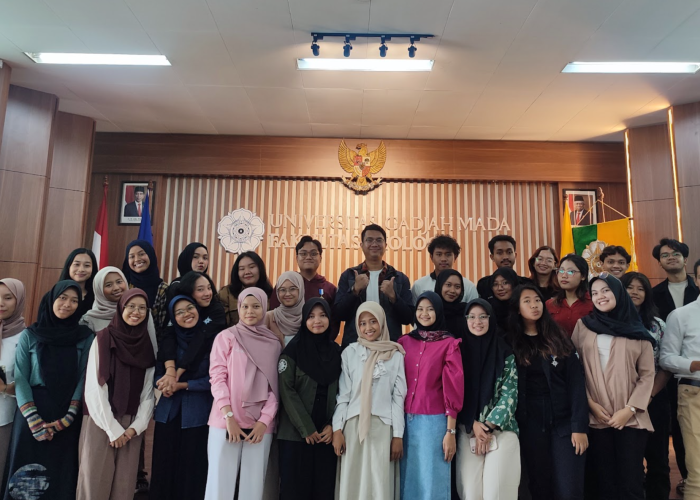
On Saturday, September 28, 2024, the Marine Study Group (KSK) of the Faculty of Biology Universitas Gadjah Mada organized the Kopdar Alumni 2024, themed “Developing Career and Further Study Plans.” This event took place at the Auditorium of the Faculty of Biology, UGM, attended by KSK Biogama members from various cohorts.
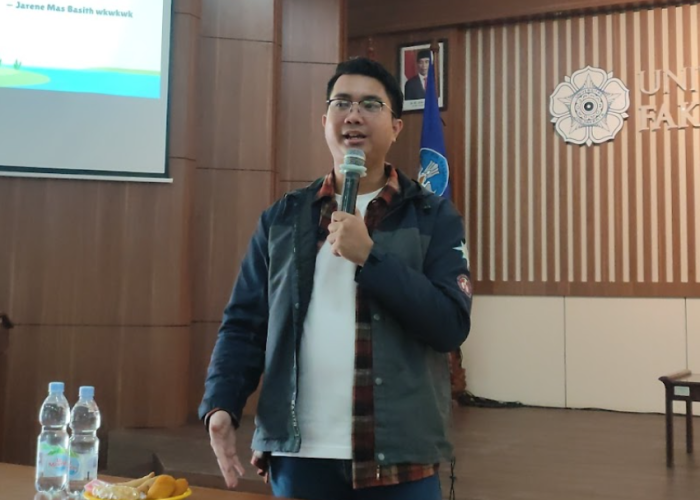
The speakers featured in this event were Basith Kuncoro Adji, S.Si., M.Sc. from the University of Birmingham, and Muhammad Arief Budhiman, S.Si. from Pertamina Foundation. They shared insights regarding their experiences after graduation, discussing topics related to further studies and career paths in environmentally focused industries. Their presentations included information on study pathways, career opportunities, and essential skills for Biology students.
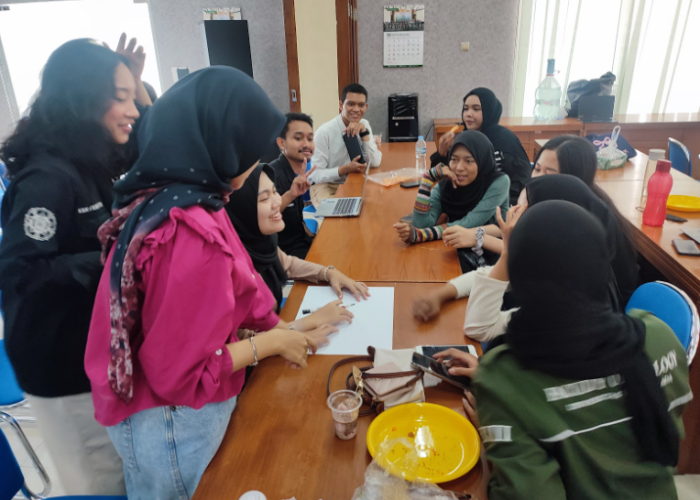
The event involved guided group discussions organized by the committee. Participants were divided into small groups to create mind maps regarding their career or further study plans. These mind maps were required to encompass information on the skills needed, career objectives, and strategies to achieve them. This group discussion lasted for 30 minutes, during which participants actively exchanged ideas and visualized their thoughts through mind mapping.
Following the group discussions, each group presented their mind maps to the speakers and the audience. The speakers provided feedback and suggestions regarding the steps that could be taken to achieve their planned career or further study goals.
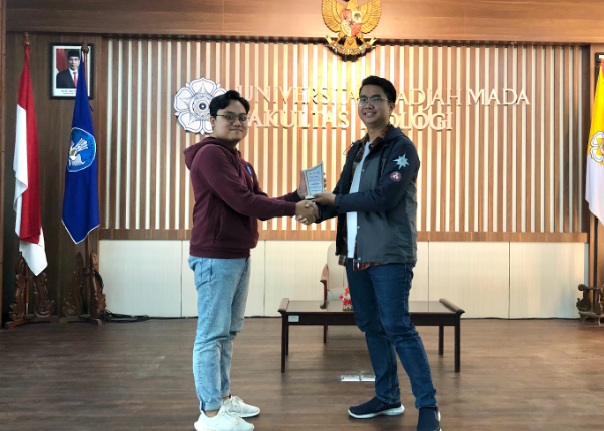
The event concluded with the presentation of mementos to the speakers in appreciation of their participation and the knowledge they shared, followed by a group photo session with all participants, both in-person and online.
The event concluded with the presentation of mementos to the speakers in appreciation of their participation and the knowledge they shared, followed by a group photo session with all participants, both in-person and online.
[Author: KSK]
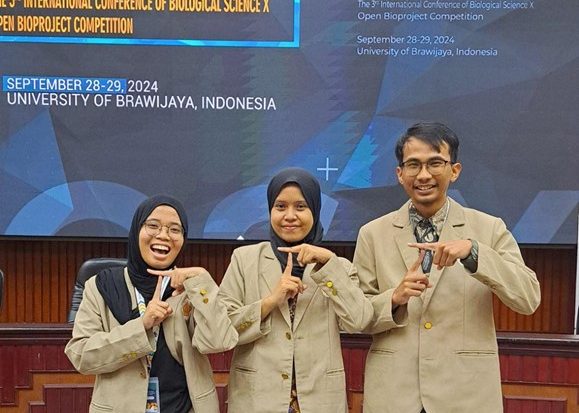
Biology students at Universitas Gadjah Mada made another achievement by winning a silver medal at the 3rd International Conference of Biological Sciences (ICoBioS) 2024. The conference, held by Universitas Brawijaya on September 27-28, 2024, had the theme “Recent Update in Bioinformatics, Synthetic Biology, and Nanobio Science for Better Future.” This success strengthens UGM’s standing in the international scientific community, particularly in driving innovation and progress in modern biological sciences. This achievement was achieved by Thoriq Abdul Halim, Tiara Putria Judith, and Salfa Athallah Agtari Nabillah students from the 2021 cohort, under the guidance of Dr. Ganies Riza Aristya, S.Si., M.Sc., Ph.D., presented research titled “Comparative Analysis of DNA Barcodes Based on Nuclear and Chloroplast Genes for Phylogenetic Reconstruction of Sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) in Java Island.”
In their presentation, the team discussed the importance of sugarcane (S. officinarum L.) production, which contributes to 80% of global sugar production. Despite Java Island supplying 61% of the national output, Indonesia only produced 2.23 million tons of sugar in 2019, while imports reached 5.46 million tons in 2021, mainly from Thailand. The low sugarcane yield is due to the narrowing of genetic diversity caused by domestication. Given the complexity of the genome and the difficulty in distinguishing morphological characteristics, the team utilized DNA barcoding techniques to analyze genetic variation in nuclear DNA and chloroplast DNA of sugarcane. This research aims to identify intra- and interspecific genetic variation among sugarcane cultivars as part of efforts to improve varietal identification, agricultural productivity, and food security in Indonesia.
The theme and goals of this research align with UGM’s commitment to supporting the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDGs No.2 on ending hunger and enhancing food security, and SDGs No.12, which focuses on sustainable production and consumption through efforts to increase sugarcane productivity and reduce dependence on sugar imports in Indonesia.
The Biology Orchid Study Club (BiOSC) of the Faculty of Biology, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), held its second Studium Generale event titled “Orchid Identification through Flower Dissection to Support Orchid Conservation in Indonesia” on Saturday, October 19, 2024, in Room 2, Building B, Faculty of Biology as part of scientific coordinators work programs, Akmal Bunyamin. The event was attended by 37 participants and aimed to enhance participants’ knowledge and skills, and motivate members in orchid identification using flower dissection to support orchid conservation efforts in Indonesia.
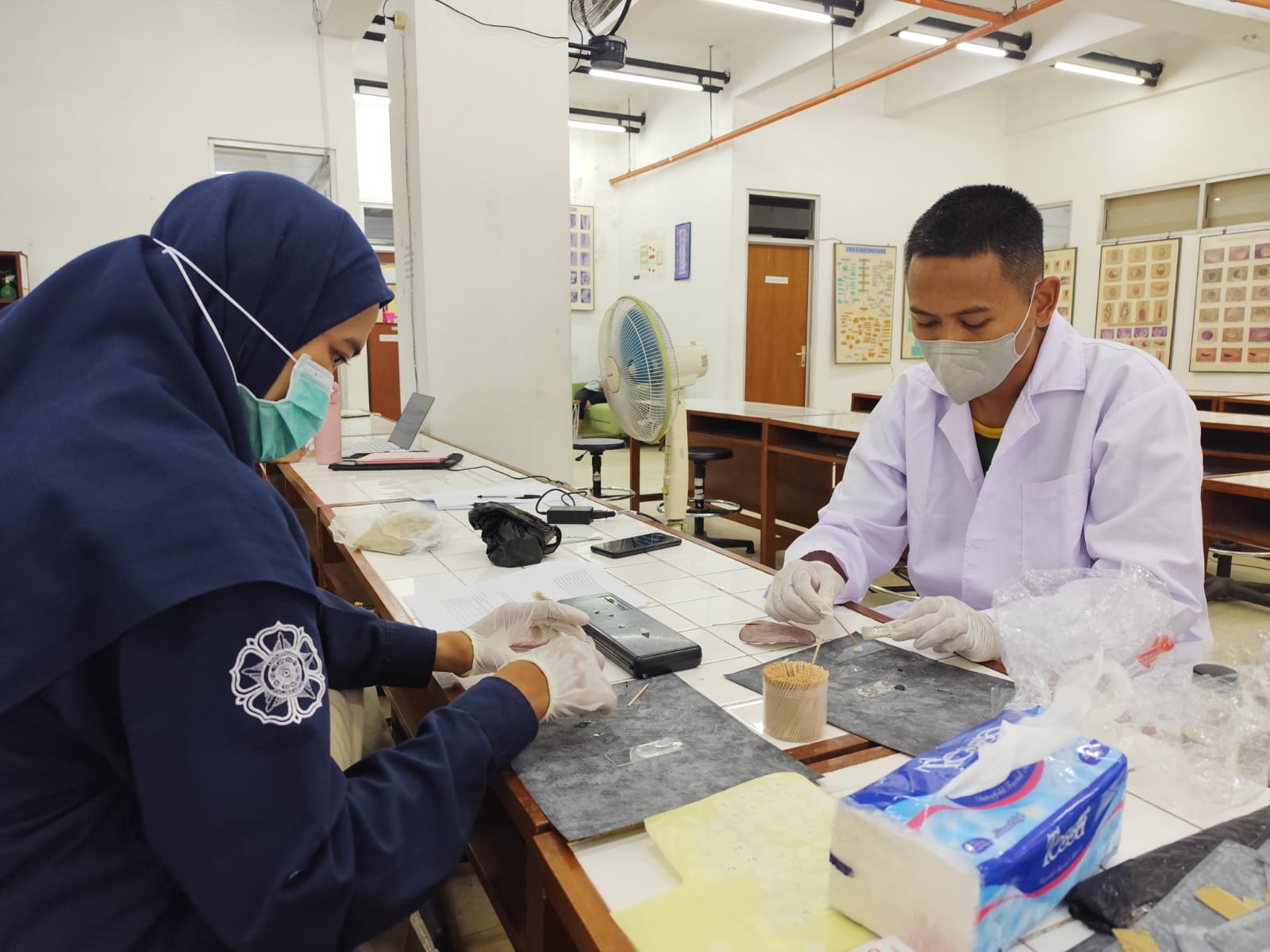
The session featured a presentation by Ms. Aninda Retno Utami Wibowo, S.Si., M.Sc., a researcher at the National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN) specializing in biosystematics, who led participants through a detailed, step-by-step guide to identifying new orchid species. Following the theoretical presentation, participants engaged in hands-on dissection practice, where each member received an orchid flower to examine. They were tasked with identifying, measuring, and meticulously documenting various flower parts, highlighting distinguishing characteristics among different orchid species.
The event proceeded smoothly with enthusiastic participation, including an interactive discussion session between attendees and the speaker. The Studium Generale aims to deepen participants’ understanding of orchid identification processes and flower dissection techniques, fostering the scientific knowledge and commitment necessary to contribute to orchid conservation efforts in Indonesia.
Written by: BiOSC
Written by: BiOSC
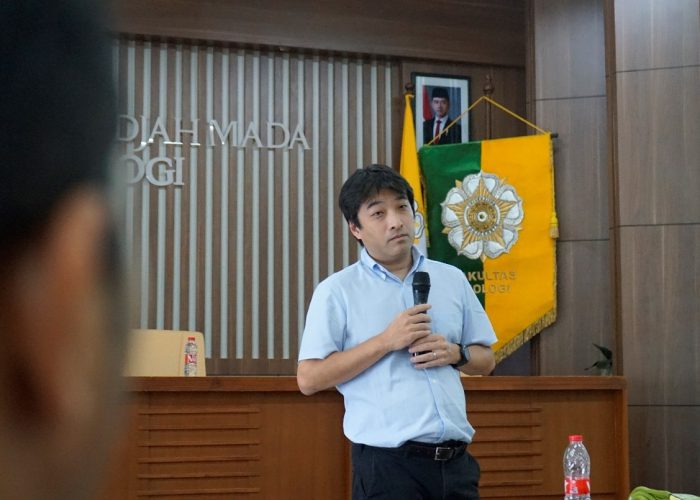
Yogyakarta, 28 October 2025 – Faculty of Biology UGM held a guest lecture featuring a plant engineering expert from Okayama University Japan, Prof. Yoji Kawano. The lecture took place in the Tropical Biology Auditorium, Faculty of Biology, UGM and was attended by students and lecturers from the Faculty of Biology, UGM.
Dr. Bambang Retnoaji, M.Sc. as Vice Dean for Academic and Student Affairs, Faculty of Biology, gave his speech at the guest lecture Monday (28/10) morning. He said that the Faculty of Biology welcomed Prof. Yoji and opened various research and academic collaboration potential with Okayama University, especially the Institute of Plant Science and Resources. Dr. Bambang also told students to gain as much knowledge as possible from the lecture.
Prof. Yoji Kawano is a Professor from the Plant Immune Design Group, Institute of Plant Science and Resources, Okayama University, Japan. His research focuses on plant pathology, immunobiology, inflammation, and phytopathology.
In this lecture, Prof. Yoji gave a presentation entitled “Deciphering Rice Immunity”. The lecture was guided by a lecturer from the Faculty of Biology from the Biochemistry Laboratory, Dr. Yekti Asih Purwestri, whose research also focuses on the development of rice plants.
Prof. Yoji explained about diseases in plants, especially rice, which are caused by fungi and how this condition is a concern in the agricultural world because of minimal information on interactions between plants and microbes. The professor, who is also an expert in plant engineering, conveyed his research which developed plant breeding using the R (NLR) gene. It is hoped that his various research efforts can contribute to applied agricultural science to obtain superior varieties that are resistant to various pest and disease threats.
The participants were enthusiastic about attending the lecture and were critical in the subsequent question and answer session. Through this public lecture, it is hoped that it can encourage innovation, especially for the academic community, in contributing to research on sustainable ecosystem preservation (SDG 4 and 15) through collaboration between the Faculty of Biology UGM and Okayama University (SDG 17).
Thursday, October 24, 2024, The Faculty of Biology, Universitas Gadjah Mada, held a Graduation Ceremony for the Postgraduate Program 2024/2025 period I at 01.00 p.m. The event was attended by the Vice Dean for Academic and Student Affairs, Dr. Bambang Retnoaji, M.Sc., the Vice Dean for Finance, Assets, and Human Resources, Dr. Slamet Widianto, S.Si., M.Sc., the Vice Dean for Research, Community Service, Collaboration and Alumni Affairs, Dr. Eko Agus Suyono, S.Si., M.App.Sc., the Head of Master in Biology Study Program, Prof.Dr.rer.nat. Andhika Puspito Nugroho, S.Si., M.Si., and the Head of Doctor in Biology Study Program, Prof. Dr. Endah Retnaningrum, M.Eng. and thesis supervisor of the graduates. The ceremony was opened by the Dean of the Faculty of Biology Prof. Dr. Budi Setyadi Daryono, M.Agr.Sc., and followed by singing Indonesia Raya, Hymne Gadjah Mada, and Faculty of Biology March. The event continued with performances of the traditional dance “Sarikalayu” from Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta.
Then, the graduation report was delivered by the Head of the Master in Biology Study Program, Prof.Dr.rer.nat. Andhika Puspito Nugroho, S.Si., M.Si.. Up to this period, the Postgraduate program of Biology UGM had graduated 138 doctoral students and 1764 master students. In the I Period of the Academic Year 2024/2025, there were two graduates for the doctoral program, Dr. Nadya Sofia Siti Sa’adah, S.Si., with cumlaude predicate, and Dr. Ainun Nikmati Layli, S.pd., M.Sc. with very good predicate. The average length of study was 3 years and 11 months and GPA of 3.95. There were 33 graduates for the master’s program with the highest GPA was 3.99.
Next, representatives of the graduates, Hayu Swari Allimi, S.Si., M.Sc., gave a speech. She expressed her gratitude to the parents, the lecturers, and all graduates for supporting their academic journey. She underscored that graduation is the beginning of a greater contribution to the field of study. As postgraduate alumni, they are expected to be leaders and solve issues in the country. She congratulated the graduates and wished their achievements would motivate them to make continuous contributions and advancements in science and technology.
The ceremony continued with a remark from the representative of the parents, Mr. Suyarto, S.T…, father of Hayu Swari Allimi, S.Si., M.Sc. He congratulated and praised the graduates for completing their studies with exceptional excellence. He extended heartfelt thanks to the faculty of biology, lecturers, and academic staff. He also reminded the graduates that their achievements are not the end of their educational journey. The path they have traveled has not been easy, but behind the difficulties, there are many opportunities for personal growth and the development of their mindset. Lastly, he expressed his hope that the lecturers would be blessed by Allah SWT for the knowledge they have imparted to the students.
The ceremony continued with a pin awarding as a sign of membership in the Faculty of Biology Family by the Vice Dean for Research, Community Service, Collaboration and Alumni Affairs, Dr. Eko Agus Suyono, S.Si., M.App.Sc., represented by graduates Dr. Nadya Sofia Siti Sa’adah, S.Si., and Muhammad Rivaldi, S.Pd., M.Sc. Following that was a speech by the Dean, Prof. Dr. Budi Setiadi Daryono, M.Agr.Sc. He congratulated the graduates and their parents. He expressed the faculty’s hope that the graduates would remain optimistic in contributing to the development of Indonesia Emas 2045. He also noted that not everyone, especially those as young as the present graduates, could complete their master’s or doctoral studies. In this period, the youngest doctoral graduate at UGM, aged 26, was from the Faculty of Biology, and thus the graduates should be grateful for their achievements. However, he reminded them not to be complacent but to continue their studies and professional pursuits.
He concluded his address with a poem: “The fruits of perseverance, patience, and strength have brought the graduates to this long-awaited day, a day that was once a dream. Families share in the pride, strengthened by the sincere prayers of parents. In the quiet of the night, prayers are offered without pause. The first step has been achieved. Strengthen the dreams and aspirations to be attained. Though change and challenges lie ahead, fear not, for you are well-prepared. Knowledge is action, and action must be guided by knowledge. To face change head-on and the dynamics of the times, clothed and embraced in comfort, nurturing one another with love and support. A spirit of togetherness is our strength. Together, we create the beauty of life. Welcome, graduates, to the family of Gadjah Mada University Alumni (KAGAMA).”
The event continued with a presentation of mementos from the graduates of Period I, Academic Year 2024/2025, represented by Giano Excelsis Pangemanan, S.Si., M.Sc., to the Dean of the Faculty of Biology UGM. The ceremony ended with a prayer by Mr. Sumarno, S.Si., M.Sc., and a group photo. [Author: KMP Biology]
Yogyakarta, 25 October 2025 – Faculty of Biology UGM held a guest lecture featuring a wildlife conservation expert from the Australian National University (ANU), Australia, Dr. George Olah. The lecture took place in the Tropical Biology Auditorium, Faculty of Biology, UGM and was attended by students and lecturers from the Faculty of Biology, UGM.
“This is a good opportunity for ongoing collaboration between the Faculty of Biology UGM and the Australian National University, Australia” Dr. Bambang Retnoaji as Vice Dean for Academic and Student Affairs in his speech Friday (25/10). Dr. Bambang also did not forget to tell students to actively seek knowledge during the lecture.
Dr. George is a wildlife conservation expert from ANU’s Fenner School of Environment and Society. His research focuses on tropical ecology, genetic conservation, and conservation management, especially bird conservation. Dr. George is also involved in various conservation projects in Indonesia, one of which is the Indonesian Parrot Foundation.
Dr. George explained his lecture presentation with the title “The role of conservation genetics in the study of parrot conservation”. Ecologists and conservation experts convey the phylogeny of the parrot tree, to the status that some species are on the verge of extinction. The threat of extinction is caused by agricultural activities, hunting, deforestation, climate change, the presence of invasive species, and human activities that affect the existence of parrot. Another big threat is the rampant illegal trade in exotic birds. ASEAN and Indonesia itself are one of the locations where this illegal trade is rampant. Dr. George invited students to be aware and participate in efforts to overcome the illegal trade in wild animals through various conservation efforts and increasing public awareness.
The participants were enthusiastic about attending the lecture and were critical in the subsequent question and answer session. Through this public lecture, it is hoped that it can encourage innovation, especially for the academic community, in contributing to research on sustainable ecosystem preservation (SDG 4 and 15) through collaboration between the UGM Faculty of Biology and the Australian National University (SDG 17).