SDG 3 : Establish Good Health and Well-Being
On Sunday, 8th October 2023, the Pengabdian kepada Masyarakat – Merdeka Belajar Kampus Merdeka (PkM-MBKM) Faculty of Biology, UGM 2023, 5 undergraduate students of Faculty of Biology, UGM class of 2020, namely Arba’ Ramadhani Artik, Arneta Yuvita, Ester Dewanti Yovita Wardani, Fadiah Sri Rahayu, and Zidni Meirizka Utami supervised by Dr. Ardaning Nuriliani, S.Si., M.Kes. and Ms. Nurini Aru Sudarsi as the partner mentor have carried out the socialization activities to the residents in Pajangan, Wedomartani Village, Ngemplak, Sleman, Yogyakarta. The theme of the socialization was “Improving the Community’s through Optimizing of Vacant Land”. This program aims to engage the community to improve the economic condition of the family by utilizing vacant land in the yard area of the house to plant vegetables, fruits, herbs, and several medicine and functional plants or also called “TOGA”. In this activity, we invited Mr. Panggih Dwi Atmojo, S.T. as a speaker. He is an alumnus of the Faculty of Engineering, UGM who is currently active as an agro economic practitioner as well as the founder and owner of Agro Edukasi Caping Merapi Yogyakarta which is located at Kenayan, Wedomartani, Ngemplak, Sleman Regency, Yogyakarta Special Region. The given presentation discussed topics about food gardening, including vegetable garden cultivation, as well as rising fish, chickens, and other small livestock to meet daily food needs. He also discussed about urban farming, which is the method of farming in the city or on limited land. In addition, the speaker also emphasized that the use of vacant land as a food garden can provide various other benefits, such as the community can provide traditional medicine independently, add decoration to the garden, provide refreshing activities through gardening, obtain healthier food that is free from chemical fertilizers, and produce biofertilizer which can be obtained through composting, eco lindi, and manure systems. This can also serve to overcome the problem of handling organic waste.
This socialization was attended by around 20 residents and received a very positive response, even some residents were very enthusiastic and directly involved in the discussion session together with the speakers.
A team of Biology students at Gadjah Mada University (S1) made another achievement at the national level by winning first place in the National Essay Competition, led by Ghefira Nur Fatimah along with Jauza Hanifah Azzahra, Meinawa Amaliah, Fadilla Nur Hidayat, and Nimas Ayu Pramesthi. This national-level essay competition was organized by Brawijaya University from June 1st to September 13th, 2023, with the theme “Collaborative Nation-Building through Applied Technology Innovation towards Self-Reliant Indonesia,” . This event encompassed various stages, including the submission of works, assessment, finalist announcement, video presentation submission, video presentation assessment, and winner announcement.
The team took the subtheme Food and Agriculture Processing Technology, with their work titled “Organic Capsule Fertilizer Made from Household Organic Waste as a Manifestation of Circular Economy and Environmental Conservation.” Their scientific work was motivated by the escalating issue of waste accumulation in Indonesia, a country that generates approximately 21.2 tons of waste per year, predominantly consisting of household waste such as food waste, dry leaves, wood, tree branches, and food industry waste. Among the household waste types employed by Ghefira and her team was the mangrove crab shell waste (Scylla serrata). The mangrove crab’s body is primarily composed of its shell, accounting for about 80% of its weight, with the remaining 20% being edible flesh. They selected the mangrove crab shell due to its biocompatible, biodegradable, low toxicity, easy synthesis, and safe application properties.
In their innovation, Ghefira and team implemented two technologies: vermicomposting and microwave technology. This combination transformed organic waste into an innovative product: water-soluble organic capsule fertilizer. The organic fertilizer was crafted from household organic waste, while the water-soluble capsule shell was created from mangrove crab shells. The vermicomposting technology was utilized in the production of organic fertilizer involving the use of earthworms, specifically Eisenia foetida and Eisenia Eugeniae, in composting organic matter. The end result of vermicomposting technology is vermicompost, a mixture of worm castings and compost.
The microwave technology was used in producing water-soluble capsule shells using mangrove crab shell material. Chitin compounds found in mangrove crab shells can be transformed into chitosan for capsule shell production. The chitosan from mangrove crab shells has a large molecular weight, necessitating the application of microwave technology to produce chitosan with high deacetylation degree and low molecular weight, ensuring high solubility in water. The process for making chitosan capsule shells involves several sequential steps, including sample preparation, chitin isolation (deproteinization, demineralization, and decolorization processes), chitosan synthesis (repeated deacetylation using microwave), production of Glucosamine Hydrochloride (GLcN HCl) (via hydrolysis and centrifugation processes), and finally, capsule shell formation using modified capsule molds.
Through these two technologies, they produced water-soluble organic capsule fertilizer with numerous advantages. The use of fertilizers that previously required mixing various components may now be simplified through the capsule form, making application on plants more convenient. Individuals need not worry about measuring fertilizer quantities, as the organic capsule fertilizer already contains all necessary elements for plants in a complete and precise manner. Additionally, the capsule form facilitates storage due to its relatively small size, saving storage space. The water solubility of the organic capsule fertilizer is relatively fast, preventing residual waste during use. Therefore, the organic capsule fertilizer implements a circular economy system and is anticipated to contribute to environmental conservation.
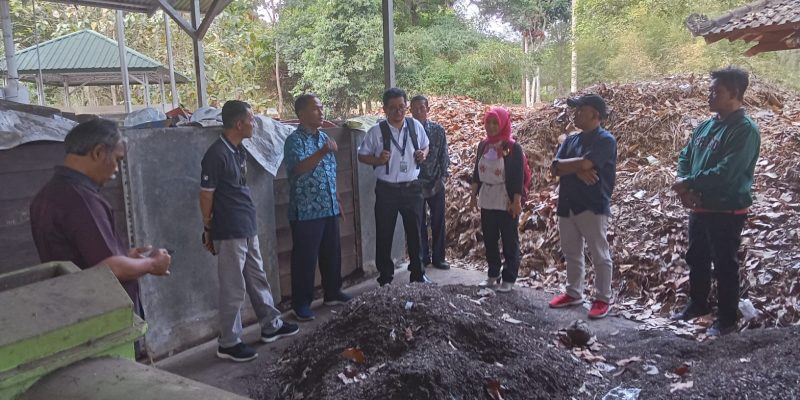
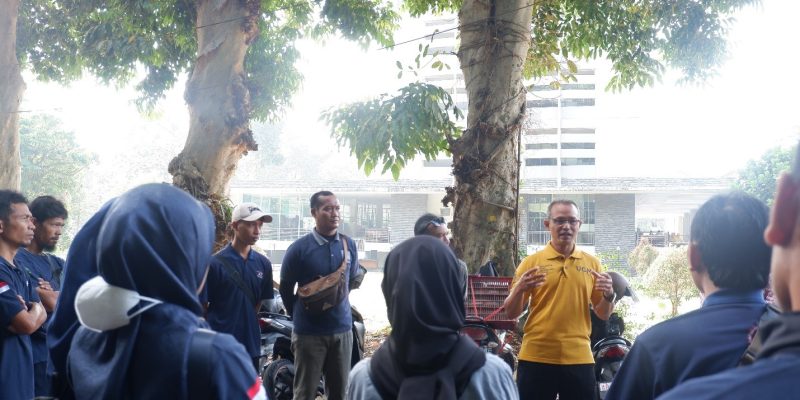
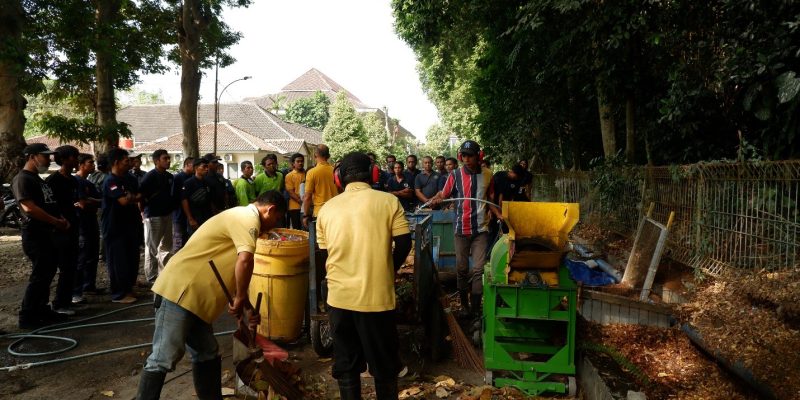
On Monday 7 August 2023, a group of waste management tour participants coordinated by SONJO, a humanitarian movement focused on aiding communities visited The Faculty Of Biology UGM. The group, consisting of 25 participants, arrived at the Faculty of Biology UGM around 9:30 AM and was promptly received by the Dean and the faculty members. This visit to the Faculty of Biology at UGM was part of a series of visits that had previously taken place at the Faculty of Dentistry at UGM.
During his welcoming speech, the Dean of the Faculty of Biology UGM, Prof. Dr. Budi S. Daryono, M.Agr.Sc., expressed gratitude for the participants’ visit. “The issue of waste actually originates from humans themselves, so it’s up to humans to solve it,” Prof. Budi stated. Furthermore, Prof. Budi elaborated that the Faculty of Biology UGM engages in daily waste management across a substantial area, including organic waste from the Biology Forest. Over time, the Faculty of Biology has made discoveries in waste management, such as expediting compost production.Following this, a video demonstrating the waste management procedures carried out at the Faculty of Biology at UGM was played.
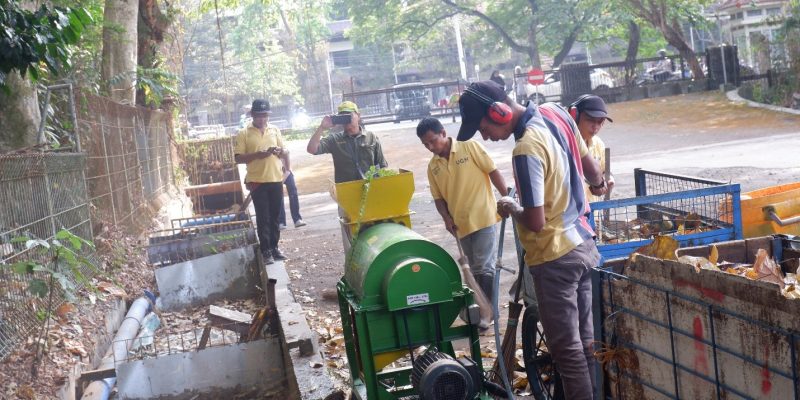
At the conclusion of the event, participants were taken to the field to witness the waste management processes firsthand, which included:
- Composting and maggot cultivation
- Production of POC/Biofertilizer and ECO enzymes
- Vermicomposting process
The waste management tour participants are scheduled to continue their visit for a period of 3 days until Wednesday (8/9/23), with participants from hospitals and religious boarding schools.
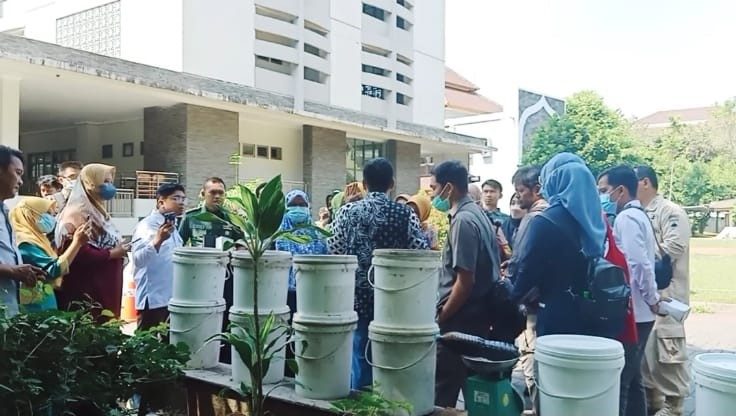
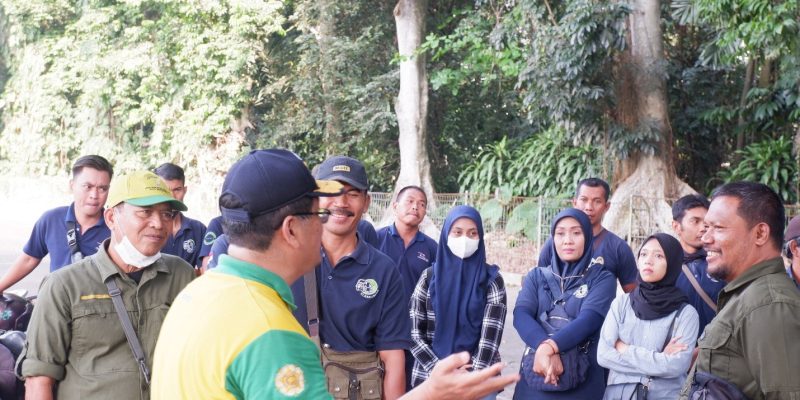
Yogyakarta, 25 August 2023 – The Organic Waste Management Training was again held by the Faculty of Biology. On this occasion, 50 participants consisted of groups from the Market Sector Department, Trade and Industry Agency (Disperindag), Special Region of Yogyakarta (DIY) as well as the Faculty of Pharmacy and Academic Hospital of Universitas Gadjah Mada. Disperindag’s participation in this training is related to waste management in 29 markets in DIY after the temporary closure of the Piyungan Final Disposal Site (TPA) months ago. At least 9 tons of waste are generated every day from the entire market which has not been managed properly.
“There needs to be an effort downstream with education and upstream by sorting and selecting the waste that is disposed of,” said the Dean of the Faculty of Biology, Prof. Dr. Budi Setiadi Daryono, M.Agr.Sc., in his speech to the training participants, Friday (25/8). Prof. Budi also said that if people at the household level were disciplined in sorting waste based on its category (organic-inorganic) it would be enough to reduce waste problems.
The Faculty of Biology has held Organic Waste Management Training activities which are attended by at least 25 Hospitals, 17 Islamic Boarding Schools, and 30 Waste Management Communities in DIY. On this occasion, as many as 40 participants from the Trade and Industry Agency, especially the Market Sector Department, attended training in the framework of solving waste problems in DIY markets, especially market organic waste in the form of fruit and vegetable waste. The training took place guided by Soenarwan Hery Poerwanto, S.Si., M.Kes. and Suharjita.
Susilo, Operational Service Manager for the DIY Disperindag People’s Market who also attended the training said that there were at least 29 markets involved and planned to work with the Faculty of Biology in waste management. He stated that the waste collected in each market usually does not only come from traders but also from the surrounding community with the largest amount of waste found in Giwangan Market and Beringharjo Market. Efforts that can be made by the Market Management since the closing of the TPA include limiting the amount of waste that the community disposes of at the market. Susilo also revealed the lack of public education regarding waste sorting and processing.
Faculty of Biology is committed to solving organic waste problems in DIY. In managing waste from DIY markets, Faculty of Biology can collect at least 3 tons of waste every day from these markets and process it. With the waste management technology applied at the Faculty of Biology including vermicomposting and Black Soldier Fly, Eco Enzyme, Bioferlilizer, Eco Lindi and others, the waste degradation process can last at least one week.
The commitment of the Faculty of Biology in waste management which also targets the people and communities in DIY emphasizes their commitment as an environmentally friendly campus and supporting Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Support for the SDGs includes increasing a healthier life (SDGs 3), having an impact on the availability of clean water in the environment (SDGs 6), and contributing to tackling climate change due to the impact of greenhouse gas emissions from organic waste piles (SDGs 13).
Yogyakarta, August 24, 2023 – The Faculty of Biology at Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM) was enlivened by the visit of 15 alumni from the Class of 1969. The purpose of this visit was to celebrate nostalgia and strengthen the bonds of camaraderie.
The warm welcome of these alumni was led by Prof. Dr. Budi Setiadi Daryono, M.Agr.Sc., the Dean of the Faculty, Dr. Bambang Retnoaji, M.Sc., as the Vice Dean for Academic and Student Affairs, and Dr. Eko Agus Suyono, M.App.Sc., as the Vice Dean for Research, Community Service, Collaboration, and Alumni, in the Biologi Tropika Auditorium of the Faculty of Biology UGM. This visit became an extraordinary moment to build networks among the alumni and the academic community of the Faculty of Biology.
Dean Budi Setiadi Daryono expressed, “We are honored and delighted to welcome back the alumni of the Class of 1969 to our campus. Their visit is a tangible testament to the enduring spirit of the Faculty of Biology UGM within our alumni.”
Furthermore, the Vice Deans provided explanations about academic developments, research, and new facilities at the Faculty to the alumni. The visit also included a campus tour, visiting Room IV, one of the classroom spaces that is still active and used to reminisce about the beautiful moments during their studies and share interesting stories. A highlight of the visit was the tour to Biomart, where the alumni could observe innovative products derived from waste processing at the Faculty of Biology UGM.
The Faculty of Biology UGM has produced various sustainable and environmentally-friendly products, such as compost fertilizer from leaf litter, probiotic fertilizers, and Liquid Organic Fertilizer (LOF). The enthusiasm of the alumni was evident as they witnessed the tangible contributions of the Faculty of Biology UGM in addressing environmental challenges, which have recently garnered attention in the city of Yogyakarta.
The visit of the alumni from the Class of 1969 to the Faculty of Biology UGM today serves as evidence that the academic spirit and camaraderie remain deeply ingrained in every facet of the development of the Faculty of Biology UGM.